Malaysia's digital landscape is undergoing a significant transformation with the introduction of e-invoice, led by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM). Launched in March 2023, e-invoice mandates businesses to adopt electronic invoicing for B2B, B2G, and B2C transactions. This initiative is designed to streamline tax processes, boost efficiency, and foster greater transparency between businesses and regulatory bodies.
The commission of e-invoicing in Malaysia is proceeding in phases. Initially, corporations with an annual turnover surpassing RM100 million must yield the e-invoicing ruling by August 1, 2024. This phased approach ensures businesses of all sizes have adequate time to adapt their processes and meet the new requirements.
Beyond ensuring compliance, e-invoicing Malaysia addresses critical challenges such as tax evasion and inaccuracies in tax reporting. Leveraging real-time approvals and automation enhances the accuracy and reliability of tax submissions, creating a fairer tax system that levels the playing field for all businesses.
Moreover, e-invoicing in Malaysia supports the country's broader vision of building a strong digital economy. Its adoption leads to streamlined operations, reduced costs, and improved financial management. It also enhances Malaysia's digital reputation, driving sustainable economic growth and progress.
What is an e-invoicing in Malaysia?
In e-invoicing Malaysia, an e-invoice is a digital document that captures transaction details between a buyer and a seller. It is a computer-readable format containing essential information such as buyer and seller details, transaction dates, applicable taxes, and payment terms. Unlike traditional paper or PDF invoices, e-invoices are shared electronically through the MyInvois Portal or API, allowing real-time validation by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM).
The e-invoicing Malaysia system uses a Continuous Transaction Control (CTC) model, where IRBM Malaysia validates invoices before buyer delivery. It ensures compliance, reduces errors, and prevents fraud, with e-invoices generated in XML or JSON formats as per Malaysia's e-invoice SDK standards.
All business transactions in Malaysia are required to adopt e-invoicing Malaysia, covering Business-to-Business (B2B), Business-to-Government (B2G), and Business-to-Consumer (B2C) interactions. The rollout is phased, starting with large enterprises earning over RM100 million annually, followed by medium and smaller businesses.
The primary goal of e-invoicing Malaysia is to simplify tax compliance, reduce tax evasion, and enhance the efficiency of tax reporting. The system helps businesses automate processes, minimize manual errors, and provide real-time financial updates.
By adopting e-invoicing in Malaysia, the country is modernizing its tax framework and aligning it with global digital standards. Through e-invoicing in Malaysia, businesses can streamline operations and achieve improved accuracy in their financial processes.
Legal Framework and Regulatory Authority for E-Invoicing Malaysia
Malaysia's e-invoicing Malaysia system, empowering the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN/IRBM) to enforce compliance. This legal mandate ensures businesses align with tax regulations and supports Malaysia's transition toward a digital economy.
Key Regulatory Authorities
The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM)
- Role: IRBM Malaysia oversees the real-time validation of e-invoices submitted through the MyInvois platform or API integration. It ensures tax compliance, reporting accuracy, and enforcement of penalties for non-compliance.
- Guidelines: IRBM Malaysia has released the e-Invoice Malaysia Software Development Kit (SDK), outlining business technical specifications.
Ministry of Finance (MoF)
- The MoF provides the broader financial policies and frameworks supporting the implementation of e-invoicing in Malaysia.
- It collaborates with IRBM to integrate e-invoicing Malaysia into Malaysia's tax and economic strategies.
Legal Mandates
- Businesses must validate all B2B, B2C, and B2G transactions via the MyInvois system to comply with Regulations.
- Validated e-invoices must be retained digitally for seven years for audit and tax compliance purposes.
Comparison With Global E-Invoice Systems: Malaysia vs PEPPOL
Real-Time Validation vs. Standardization
Malaysia emphasizes real-time invoice validation through the MyInvois platform before invoices are shared with buyers, aligning with e-invoicing Malaysia compliance needs. PEPPOL focuses on standardizing invoice formats for seamless cross-border transactions.
Phased Rollout
E-invoicing Malaysia implements a phased rollout, starting with large enterprises and gradually including MSMEs, ensuring a structured approach. PEPPOL, however, offers a universal framework applicable to all businesses, regardless of size.
Domestic vs. Cross-Border Focus
Malaysia's system is tailored to local compliance needs while paving the way for future global interoperability under e-invoicing Malaysia. PEPPOL prioritizes cross-border standardization, facilitating international trade.
Simplified Tools for MSMEs
Malaysia's MyInvois portal supports manual uploads and batch processing, simplifying e-invoicing Malaysia's adoption for smaller businesses. PEPPOL's framework, in contrast, requires advanced system integration, catering to enterprises with technical resources.
Benefits of Implementing E-Invoice in Malaysia
Enhanced Tax Compliance with Real-Time Validation
E-invoicing Malaysia minimizes errors in tax reporting and ensures alignment with IRBM Malaysia standards, reducing audit risks and penalties. Errors are quickly identified and rectified, leading to more accurate and faster tax reporting.
Streamlined Operations and Improved Operational Efficiency
Automating invoicing processes through e-invoicing Malaysia reduces manual efforts, human errors, and processing times. Businesses can enhance productivity, handle transactions more efficiently, and cut costs by moving away from traditional paper-based systems.
Real-Time Financial Insights to Support Smarter Business Decisions
E-invoicing Malaysia integrates seamlessly with data analysis tools, offering immediate insights into cash flow. Businesses can use these real-time insights to make informed decisions and manage finances with up-to-date information.
Strengthened Global Competitiveness Through Digital Transformation
By aligning with global e-invoicing standards, e-invoicing Malaysia enhances trust and facilitates international business transactions. This adoption strengthens Malaysia's worldwide standing and enables businesses to expand their reach internationally.
Tailored Support for MSMEs with Gradual Implementation
E-invoicing Malaysia supports small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) with a phased implementation approach, giving them the time and tools needed for a smooth transition. This system helps MSMEs streamline operations, access government incentives, and adopt industry best practices efficiently.
E-Invoice Malaysia Timeline
Phase | Applicable Businesses | Deadline | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
Phase 1 | Businesses with annual turnover > RM100 million | August 1, 2024 | Large enterprises with the capability to lead the adoption of e-invoicing as a compliance measure. |
Phase 2 | Businesses with turnover RM25 - RM100 million | January 1, 2025 | Medium-sized businesses provided additional time to upgrade systems and adapt to requirements. |
Phase 3 | Businesses with turnover > RM150,000 | July 1, 2025 | Small businesses and MSMEs phased in last to ensure a smooth transition without operational overload. |
Step-Wise Implementation Plan for E-Invoicing Malaysia
March 2023:
The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) has announced the obligatory e-invoicing of the Malaysian industry.
Businesses are given clear guidelines and timelines to prepare for phased implementation.
Phase 1: August 1, 2024:
Who: Large enterprises with annual revenues exceeding RM100 million.
Objective: Early adoption by major players to set the groundwork for system integration and industry adaptation.
Phase 2: January 1, 2025:
Who: Medium-sized enterprises with annual incomes between RM25 million and RM100 million.
Objective: Provide these businesses with time to upgrade their invoicing systems, ensuring compliance while minimizing disruptions.
Phase 3: July 1, 2025:
Who: Small businesses and MSMEs with annual revenues exceeding RM150,000.
Objective: Support smaller entities through government incentives, resources, and training to facilitate their transition.
Grace Period for Compliance
The interim relaxation period in Malaysia's e-invoicing mandate allows businesses to transition. The interim relaxation period for e-invoicing in Malaysia will enable enterprises to transition without penalties, provided they show efforts toward compliance. This period will allow companies to upgrade systems, integrate with the MyInvois portal, and train staff, addressing technical and operational challenges. By offering flexibility, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) ensures a practical, disruption-free transition while encouraging early adoption and long-term compliance with the e-invoicing system.
E-Invoice Process in Malaysia
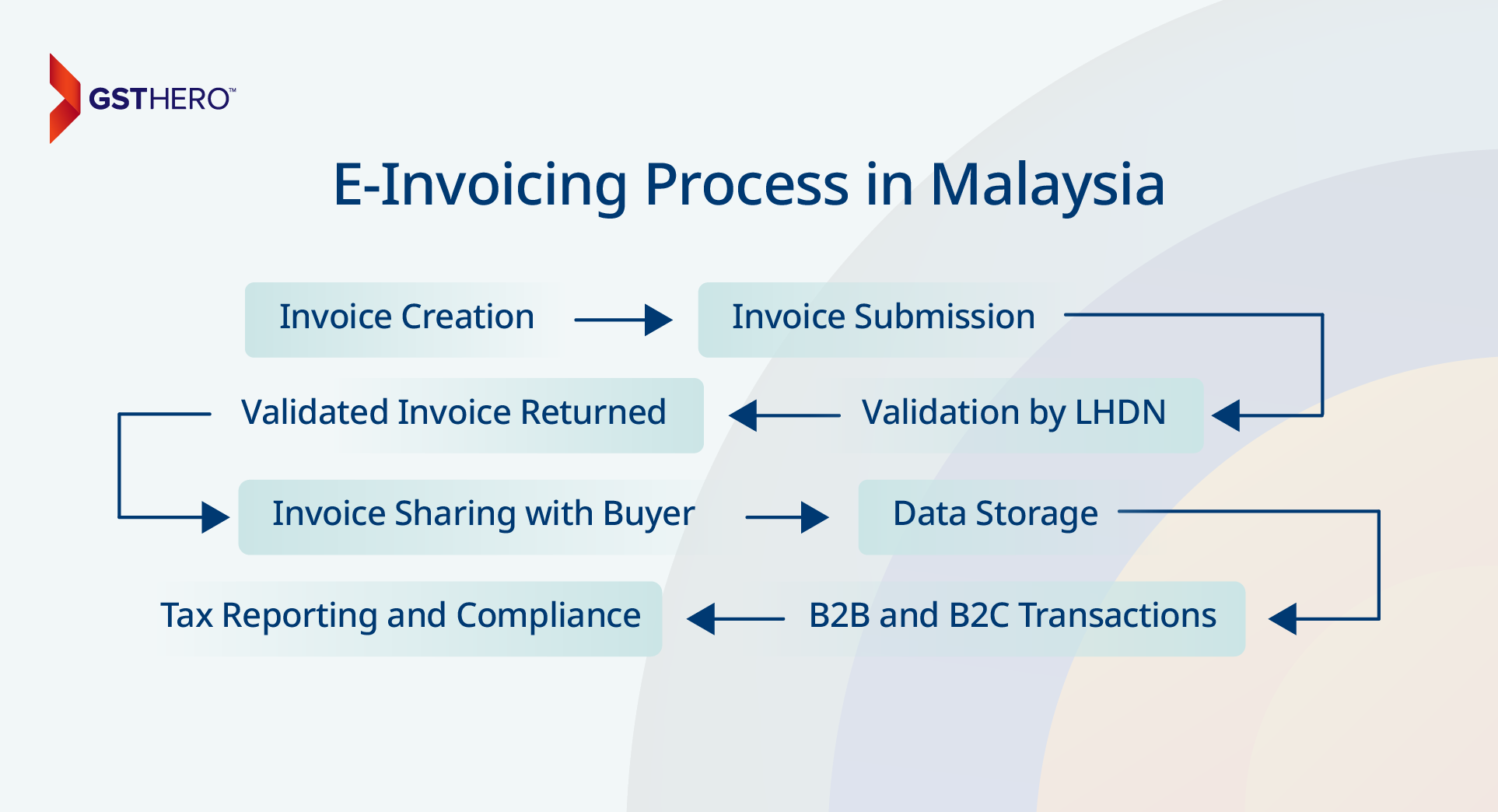
The e-invoicing Malaysia process ensures seamless compliance with LHDN requirements while enhancing invoice generation, validation, and reporting efficiency. The process is outlined below in a step-by-step manner:
Invoice Creation
The supplier creates an invoice in the required XML or JSON format, adhering to e-invoice LHDN guidelines. The invoice includes critical details such as buyer information, item descriptions, amounts, and applicable tax details.
Invoice Submission
Once generated, the supplier submits the invoice to the LHDN e-invoicing Malaysia platform through API integration for automation or the manual upload portal for businesses with limited technical resources.
Validation by LHDN
The e-invoicing Malaysia system, powered by the LHDN platform, validates invoices to ensure they meet all technical and compliance requirements. Valid invoices are issued a Unique Identifier (UUID) and a QR code, while discrepancies result in rejection, requiring suppliers to correct and resubmit.
Validated Invoice Returned
Once validated, the invoice is returned to the supplier with the UUID and QR code, confirming compliance with e-invoicing Malaysia standards.
Invoice Sharing with Buyer
The validated invoice is then transferred to the buyer. Businesses using ERP systems can seamlessly integrate the validated data for record-keeping, payment processing, and tax reporting.
Data Storage
Suppliers and buyers must store validated e-invoices for audits and future reference. This proper storage practice ensures transparency and compliance with tax regulations under e-invoicing in Malaysia.
B2B and B2C Transactions
For B2B transactions, validated invoices are integrated into ERP systems, improving accuracy and reporting efficiency. For B2C transactions, the LHDN-validated QR code on the invoice ensures compliance and accurate documentation.
Tax Reporting and Compliance
The e-invoicing Malaysia platform automatically captures validated invoice data, reducing manual errors and streamlining tax reporting. This approach improves transparency and simplifies compliance audits.
E-Invoice Models in Malaysia

E-invoicing Malaysia provides businesses with multiple methods for transmitting e-invoices, designed to cater to small and large enterprises. These methods align with businesses diverse technological capabilities and transaction volumes.
1. MyInvois Portal
The e invoice portal, known as the MyInvois platform is a convenient solution for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or companies managing lower transaction volumes. Through this platform, businesses can manually generate e-invoices one at a time or in batches using features like spreadsheet uploads. Introduced by Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri (LHDN) on June 28, 2024, the e Invoice login portal comes equipped with two functional setups: a testing environment for trial use and a production environment for live submissions. This method is particularly beneficial for businesses without advanced system integrations.
2. API Integration
Application Programming Interface (API) integration provides a robust and automated solution for larger enterprises managing high transaction volumes. By linking their ERP systems, accounting software, or billing platforms to the MyInvois system, businesses can ensure real-time generation, submission, and correction of e-invoices. To support this, LHDN has introduced the e-invoicing Malaysia Software Development Kit (SDK), offering a technical framework for seamless adoption.
Malaysia's MyInvois Platform
The MyInvois platform, introduced by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM), serves as the backbone of e-invoicing in Malaysia, streamlining invoice submission, validation, and compliance for businesses transitioning to the digital invoicing era. Businesses can access the platform via a secure e-invoice login process, ensuring only authorized users can submit and manage invoices.
Key Features of MyInvois:
Dual Environments:
- Testing Environment: Allows businesses to trial invoice submissions and system integration.
- Production Environment: Used for live, real-time invoice validation and compliance.
Submission Flexibility:
- Offers manual upload options for smaller businesses and API integration for enterprises requiring automated, high-volume invoice submissions under e-invoicing Malaysia.
Real-Time Validation:
- Ensures every invoice meets compliance standards, generating Unique Identifiers (UUID) and QR codes for traceability and accuracy.
Format Compatibility:
- Supports industry-standard formats like XML and JSON, enabling seamless integration with diverse business systems.
Secure Data Handling:
- Employs robust encryption to safeguard sensitive financial information, ensuring data integrity and privacy.
Cost-Effective Accessibility:
- The platform is free to use, offering smaller businesses an efficient solution without additional software costs.
Why MyInvois Matters:
- Simplifies Compliance: Reduces errors and rejections with automated validation, aligning with e-invoicing Malaysia goals.
- Supports All Business Sizes: From micro-enterprises to large corporations, the platform caters to varied needs.
- Enhances Transparency: Provides real-time validation, ensuring trust and clarity in transactions.
Types of e-Invoices in Malaysia
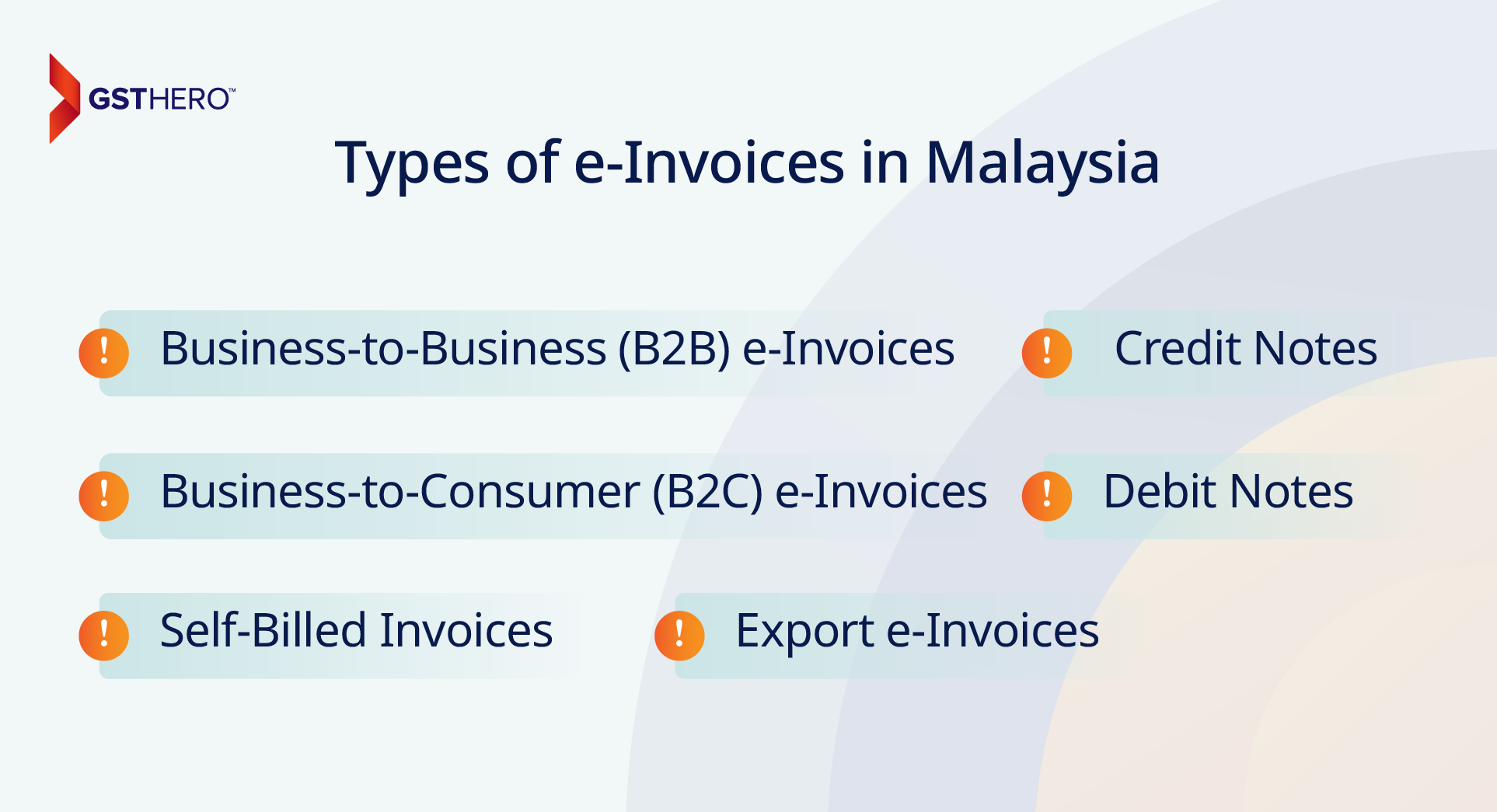
Malaysia's e-invoicing Malaysia framework accommodates various types of e-invoices to meet diverse business requirements and transaction categories. These e-invoice types ensure proper documentation, compliance, and streamlined reporting for suppliers and buyers.
1. Business-to-Business (B2B) e-Invoices
B2B e-invoices are used for transactions between businesses, such as sales of goods or services. These invoices must be sent to the e-invoice LHDN platform for validation before they are provided to the buyer. Once validated, the invoice is assigned a Unique Identifier (UUID) and a QR code.
2. Business-to-Consumer (B2C) e-Invoices
B2C e-invoices are generated for transactions between businesses and individual consumers. While the invoice validation process remains the same, the primary focus is to include a QR code to confirm compliance with e-invoice LHDN regulations.
3. Credit Notes
Credit notes are e-invoices generated when adjustments are made to previously issued invoices. They are typically used in returns, discounts, or errors in the original invoice. Businesses must submit credit notes to the LHDN platform, where they undergo validation, similar to standard invoices.
4. Debit Notes
Debit notes are issued to reflect an increase in the invoice value due to changes such as additional charges, corrections, or errors in the original invoice. Like credit notes, debit notes must be validated through the e-invoice LHDN platform before being shared with the buyer.
5. Self-Billed Invoices
Self-billed invoices occur when the buyer generates an invoice on behalf of the supplier, particularly in contractual or service-based transactions. These invoices must comply with e-invoicing Malaysia requirements, including validation via the MyInvois system and the inclusion of a QR code.
6. Export e-Invoices
Export e-invoices are generated for transactions involving the sale of goods or services to businesses outside Malaysia. These invoices are critical for ensuring accurate tax reporting and customs compliance. Export e-invoices must be validated via the e-invoice LHDN platform before being shared with international buyers.
Entities Mandated to Adopt E-Invoicing Malaysia

In Malaysia, the e-invoicing Malaysia mandate applies to various entities, ensuring inclusivity and accurate tax documentation across sectors. The mandate applies to businesses of varying sizes, ensuring inclusivity and proper tax documentation across industries.
1. Large Enterprises
Organizations with significant annual turnover are the primary focus for early adoption. These businesses are expected to integrate their existing ERP systems or accounting software with the LHDN platform via API to ensure automated, real-time invoice reporting.
2. Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Despite handling lower transaction volumes, SMEs must equally comply with Malaysia's e-invoicing mandate. They can leverage the MyInvois Portal for manual or bulk e-invoice submissions, offering a more straightforward option without requiring advanced integrations.
3. Micro Enterprises
Micro-enterprises, often with limited technical infrastructure, are also included under the compliance framework. These businesses can utilize the manual upload functionality of the MyInvois Portal to generate and validate e-invoices efficiently.
4. Cross-Border Businesses
Entities engaged in export or import activities must generate export e-invoices or validate their transactions via the LHDN platform, which will ensure accurate tax documentation for international trade and customs compliance.
5. Service Providers and Contractors
Businesses offering services or engaging in contractual agreements must issue validated e-invoices to their clients. So, it will include generating self-billed invoices when necessary and ensuring all transactions are accurately recorded in compliance with e-invoicing Malaysia guidelines.
E-Invoicing Implementation Across Industries in Malaysia
The introduction of e-invoicing in Malaysia impacts various industries differently, requiring tailored strategies to ensure compliance and operational efficiency. Each sector has specific needs and challenges that require customized solutions to streamline invoicing while adhering to the mandate. Below is a list of industries impacted by the e-invoicing system:
E-Commerce Industry
Financial Services Industry
Construction Industry
Petroleum Industry
Aviation Industry
Healthcare Industry
Telecommunication Industry
Pharmaceutical Industry
Tourism Industry
Textile Industry
Insurance and Takaful Industry
Retail Industry
Challenges Related to E-Invoicing in Malaysia

While e-invoicing in Malaysia offers significant benefits, its implementation has several challenges for businesses transitioning to the new system. These challenges can vary depending on business size, technical infrastructure, and operational readiness.
1. Integration with Existing Systems
Businesses often need help integrating their existing ERP, billing, or accounting systems with the LHDN e-invoicing Malaysia platform. Ensuring seamless API integration requires technical expertise and substantial IT resources, which can be a hurdle for many organizations.
2. High Initial Implementation Costs
Setting up e-invoicing Malaysia processes involves software upgrades, system integration, and staff training costs. These initial costs can be burdensome for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), especially those with limited financial resources.
3. Limited Technical Capabilities for SMEs and Micro Businesses
Many SMEs and micro-enterprises lack the technical expertise or infrastructure to adopt e-invoicing systems efficiently. Limited access to IT resources and technical support makes the transition particularly challenging for these businesses.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Understanding
Understanding and adhering to the e-invoicing Malaysia guidelines set by LHDN can be challenging, particularly for businesses unfamiliar with digital invoicing processes. Ensuring compliance with invoice formatting, validation rules, and timelines adds complexity.
5. Real-Time Validation and Rejections
The requirement for real-time validation through the e-invoice LHDN platform can disrupt business workflows if invoices are rejected due to errors or missing information. Businesses need to develop robust processes to identify and rectify mistakes to avoid delays quickly.
6. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
E-invoicing Malaysia involves transmitting sensitive financial data to government systems, raising concerns about data security, privacy, and the potential for unauthorized access or breaches.
7. Change Management and Training
Transitioning from manual invoicing to digital e-invoicing in Malaysia requires significant changes in internal processes. Businesses must invest in employee training and change management strategies to ensure a smooth transition and adoption of the new system.
8. Cross-Border Transactions
Managing cross-border transactions under the e-invoicing system presents unique challenges, such as handling multi-currency invoices, varying tax regulations, and compliance with both local and international trade laws.
9. System Downtime and Reliability
Businesses relying on the e-invoicing platform may face disruptions due to system downtime or technical glitches. Any delays in real-time validation can hinder transaction processing and impact overall business operations.
10. Adapting to Frequent Updates
The e-invoicing system in Malaysia is evolving, with periodic updates to guidelines, standards, and technical specifications. Businesses must continuously adapt to these changes, which can be resource-intensive and challenging to manage.
Penalties for Non-Compliance with E-Invoicing in Malaysia
Non-compliance with e-invoicing Malaysia penalty regulations can result in financial and operational consequences. These penalties ensure businesses adopt the system promptly and adhere to the rules. Below are the key areas where penalties may apply:
1. Failure to Generate and Submit E-Invoices
Businesses that fail to generate or submit e-invoices to the LHDN platform within the stipulated timeframe will face financial penalties. The exact penalty amount will depend on the delay's severity and the non-compliance frequency.
2. Submission of Incorrect or Incomplete Information
If a business submits an e-invoice with incorrect, incomplete, or misleading details, LHDN may impose fines. Includes errors in tax amounts, buyer or supplier information, or invalid formats that need to align with the e-invoice guidelines.
3. Non-Adherence to Validation Rules
Invoices that do not pass the real-time validation process due to non-compliance with the technical standards (e.g., missing XML or JSON formatting, UUID, or QR code) can lead to penalties. Businesses must ensure that all invoices are validated successfully before sharing them with buyers.
4. Delayed Implementation
Organizations that fail to comply with the phased implementation deadlines set by LHDN may incur penalties.
5. Repeated Non-Compliance
Businesses that repeatedly violate e-invoicing Malaysia regulations may face escalating penalties. Include additional fines, audits, or legal consequences, depending on the nature and frequency of non-compliance.
6. Legal Action and Audit Risks
Non-compliance can also trigger tax audits or investigations by e-invoice LHDN. Businesses may face further scrutiny, which can disrupt operations and increase compliance costs. Legal action may also be pursued for deliberate violations or tax evasion.
7. Impact on Business Operations
Non-compliance could result in reputational damage and disruptions to business relationships, as validated e-invoices are critical for seamless transactions between suppliers, buyers, and government entities.
Type of Non-Compliance | Penalty Amount | Additional Consequences |
|---|---|---|
Failure to issue or submit e-invoices | RM 200 to RM 20,000 per offence | Up to 6 months of imprisonment or both. |
Submission of incorrect/incomplete data | RM 200 to RM 20,000 per offence | Invoice rejection and mandatory resubmission |
Repeated violations | RM 200 to RM 20,000 per offence | Higher scrutiny, possible tax audits |
Delayed adoption based on deadlines | RM 200 to RM 20,000 per offence | Increased fines for prolonged delays |
Intentional non-compliance/tax evasion | RM 200 to RM 20,000 per offence | Legal action and imprisonment |
Role of E-Invoicing Solution Providers in Malaysia

E-invoicing software solution providers play a crucial role in helping businesses adopt and comply with Malaysia's e-invoicing mandate. They offer technical expertise, tools, and systems that streamline e-invoicing, ensuring seamless integration with the Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri (LHDN) platform. Their role is particularly vital for businesses of all sizes, from large enterprises to MSMEs, in achieving compliance and operational efficiency.
1. Providing LHDN-Compliant Solutions
E-invoicing solution providers develop systems that comply with LHDN's e-invoice guidelines and technical requirements, including using XML/JSON formats and real-time validation via the MyInvois system. They ensure that invoices meet the Malaysian e-Invoice Software Development Kit (SDK) standards for successful validation.
2. Seamless API Integration
Solution providers enable API integration between existing ERP, accounting, or billing systems and the MyInvois platform for businesses with high transaction volumes. Ensures real-time e-invoice generation, submission, validation, and corrections without manual intervention.
3. Customization for Businesses of All Sizes
Solution providers offer tailored solutions based on a business's size and needs. Large enterprises focus on complete automation and high-volume data handling, while MSMEs provide more straightforward tools such as manual upload features or spreadsheet-based invoicing.
4. Technical Support and Training
Solution providers deliver technical support to businesses during implementation, ensuring smooth integration and minimal disruptions. To build operational confidence, they also train internal teams on the e-invoicing process, submission workflows, and error handling.
5. Data Security and Compliance
E-invoicing solution providers implement robust data encryption and security protocols to protect sensitive invoice and financial data. They ensure compliance with data privacy laws, addressing businesses' concerns over unauthorized access or breaches.
6. Error Detection and Automation
To minimize errors, solution providers integrate automated validation tools that detect invoice inaccuracies before submission to the LHDN platform. Reduces rejection rates, ensures quick resubmission, and enhances overall process efficiency.
7. System Testing and Deployment
Solution providers assist businesses in testing their systems through the LHDN testing environment, ensuring a smooth transition to production. They troubleshoot issues, identify gaps, and deploy solutions that align with compliance requirements.
8. Ongoing Updates and Maintenance
E-invoicing solution providers monitor regulatory updates and system changes introduced by LHDN. They offer regular system updates, ensuring businesses comply with the latest e-invoicing mandates and technical standards.
9. Enhanced Reporting and Analytics
Providers integrate data analytics tools that offer real-time insights into financial data and cash flows. Enables businesses to make informed decisions, improve tax reporting accuracy, and streamline operations.
10. Supporting Cross-Border E-Invoicing
For businesses engaged in export transactions, solution providers offer tools to generate and validate export e-invoices, ensuring compliance with Malaysian and international trade regulations.
Government Incentives and Support for E-Invoicing Adoption
The Malaysian government actively supports businesses adopting e-invoicing through various incentives and assistance programs. These measures reduce implementation challenges, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), while ensuring a smooth transition to the digital invoicing system.
1. Financial Assistance for SMEs
To ease the cost burden, the government offers grants or financial incentives to help SMEs upgrade their invoicing systems. This financial support enables businesses to adopt e-invoicing without significant upfront expenses.
2. Free MyInvois Portal Access
The government has launched the MyInvois Portal, a free platform for businesses, particularly micro and small enterprises, to generate and submit e-invoices. Eliminates the need for advanced infrastructure or costly system upgrades.
3. Training and Capacity-Building Programs
The government conducts training sessions, workshops, and webinars to increase awareness and preparedness. These programs educate businesses on compliance requirements, technical specifications, and the operational benefits of e-invoicing.
4. Technical Resources and Support
The government provides technical resources, including the e-Invoice Malaysia Software Development Kit (SDK), to assist businesses with system integration. The SDK includes detailed guidelines and tools for seamless adoption of the e-invoicing system.
5. Tax Incentives for Early Compliance
Businesses adopting e-invoicing before the mandatory deadlines may be eligible for tax incentives or relief. Encourages early adoption while rewarding proactive compliance efforts.
6. Dedicated Support for MSMEs
Special provisions are made for micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) to ensure a seamless transition. These include simplified tools, easy-to-use platforms, and step-by-step guidance for e-invoicing adoption.
Advantages of API Integration Over Manual Uploads
API integration provides a seamless and automated approach to e-invoicing in Malaysia, which is particularly beneficial for businesses with higher transaction volumes. Below are the key advantages of API integration:
1. Real-Time Invoice Submission
API integration allows for the real-time submission of invoices to the LHDN e-invoicing Malaysia platform, eliminating delays in processing and validation while ensuring compliance with e-invoicing timelines.
2. Automation of Processes
With API integration, invoice generation, submission, and validation are fully automated, reducing the need for manual intervention. Saves time and minimizes the risk of human errors often associated with manual uploads.
3. Handling High Transaction Volumes
Large enterprises or businesses with frequent transactions benefit from API integration as it can process thousands of invoices simultaneously. Manual uploads could be more efficient and practical for handling high volumes.
4. Improved Accuracy and Error Reduction
API integration ensures invoices adhere to the required XML/JSON formats and real-time compliance standards. Validation errors are flagged automatically, reducing the chances of rejection and simplifying the correction process.
5. Seamless ERP System Integration
API integration connects directly with ERP systems, billing software, or accounting platforms, ensuring a smooth data flow. Eliminates the need to export or upload invoice files, improving operational efficiency manually.
Cross-Border and Export Transactions: Ensuring Global Compliance
E-invoicing Malaysia extends beyond domestic operations, playing a critical role in cross-border and export transactions. Businesses engaged in international trade face unique challenges, such as adhering to diverse tax regulations, managing multi-currency transactions, and ensuring accurate customs documentation.
Malaysia's e-invoicing framework is designed to align with international standards such as PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement On-Line). This alignment facilitates seamless cross-border invoicing by standardizing formats, ensuring real-time validation, and enhancing transparency between trading partners.
By integrating with PEPPOL and similar frameworks, Malaysian businesses
can simplify international transactions, improve compliance with global trade requirements, and foster trust with overseas stakeholders, supporting e-invoicing Malaysia's goals and the nation's broader digital economy objectives.
Future of E-Invoicing in Malaysia: Key Technological Advancements
AI-Driven Validation: Automates error detection and ensures compliance in real-time, reducing manual effort and submission errors under the e-invoicing Malaysia framework.
Blockchain Technology: Provides secure, tamper-proof invoicing records, enhancing transparency and preventing fraud in the e-invoicing Malaysia ecosystem.
Predictive Analytics: Delivers actionable insights for cash flow forecasting, tax planning, and financial decision-making, complementing the e-invoicing Malaysia system.
IoT Integration: Enables real-time data collection and automatic invoice generation from connected devices, supporting the evolution of e-invoicing in Malaysia.
Cloud-Based Platforms: Assures scalability, accessibility, and seamless partnership for enterprises using e-invoicing Malaysia.
Interoperability with Global Standards: Facilitates cross-border transactions through frameworks like PEPPOL, further aligning e-invoicing Malaysia with global trade practices.
How GSTHero Supports E-Invoicing Compliance in Malaysia

GSTHero simplifies the transition to e-invoicing in Malaysia by offering LHDN-compliant solutions that enable seamless invoice generation, validation, and submission. Designed to cater to businesses of all sizes, GSTHero automates invoicing workflows, minimizes errors, and integrates effortlessly with existing ERP systems, enhancing compliance and operational efficiency.
Key Benefits of GSTHero for E-Invoicing:
1. Seamless API Integration
Automates real-time invoice submission the MyInvois platform like SAP, Oracle, and Tally ensures automated, real-time invoice submission to the MyInvois platform.
2. Error-Free Invoice Validation
GSTHero detects and flags invoice discrepancies before submission, ensuring compliance with e-invoices LHDN's XML/JSON formats and reducing rejections.
3. High Volume Invoice Processing
Manages high-volume invoice submissions effectively, making it suitable for enterprises with substantial transaction workloads.
4. User-Friendly Tools for SMEs
For small businesses, GSTHero offers simplified tools like manual uploads, bulk invoice generation, and spreadsheet-based solutions to ensure compliance without complexity.
5. Robust Data Security
End-to-end encryption ensures sensitive financial information is protected, meeting the stringent security standards of e-invoicing Malaysia.
6. Real-Time Financial Insights
GSTHero provides real-time dashboards and analytics for better cash flow and financial decision-making visibility.
7. Faster Error Corrections
In validation failures, GSTHero simplifies error identification, allowing quick corrections and resubmission.
8. Expert Support and Training
With continuous support and thorough training, GSTHero ensures businesses seamlessly adapt to the e-invoicing Malaysia system.
Conclusion
The transformation to Malaysia e-invoicing 2024 emphasizes an important milestone in the nation's digital transformation measures. With tools like GSTHero, businesses can ensure compliance with e-invoicing Malaysia LHDN standards, streamline operations, and avoid e-invoicing Malaysia penalty risks. Early preparation and adoption of these solutions will position companies for success in this evolving digital landscape.
Solutions like GSTHero play a pivotal role in this transformation by offering seamless LHDN-compliant tools, API integrations, and user-friendly solutions for businesses of all sizes. By automating workflows, ensuring real-time validation, and enhancing financial accuracy, GSTHero enables organizations to navigate the e-invoicing mandate effortlessly.
As Malaysia continues to embrace global digital standards, businesses adopting e-invoicing in Malaysia will not only meet compliance requirements but also enhance operational efficiency, data security, and financial transparency. Early preparation and technological support will ensure enterprises stay competitive in this evolving digital landscape, driving long-term growth and sustainability.
FAQ On E-invoice Malaysia
E-invoicing is the electronic generation, transmission, and receipt of invoices in a structured data format. In Malaysia, it involves businesses submitting invoice data to the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN) for real-time validation. This allows for automated processing and verification of invoice details.
E-invoicing is crucial for enhancing tax compliance by providing the LHDN with real-time visibility into business transactions. It helps reduce tax fraud and evasion, improves the accuracy of tax reporting, and fosters a more transparent business environment. Additionally it increases business efficiency.
E-invoicing delivers numerous benefits, including faster payment processing through automated systems, reduced administrative costs by eliminating paper-based processes, improved accuracy and fewer errors due to standardized digital formats, enhanced data security and robust audit trails for better tracking, environmental friendliness through decreased paper usage, and streamlined record-keeping with easy digital storage and retrieval.
Essentially, Malaysian e-invoicing requires: following LHDN's data rules, sending invoices instantly, sticking to their rollout schedule, using approved sending methods, and having correct invoice details.
The MyInvois Portal is a free platform IRBM Malaysia provides for generating and submitting e-invoices. It is ideal for small and medium-sized businesses with limited technical infrastructure. Companies can manually create invoices or upload them in bulk using spreadsheets.
API integration lets businesses connect their ERP, accounting, or billing systems directly to the MyInvois platform. It automates the real-time e-invoice generation and validation process, reducing manual effort. API integration ensures accuracy, compliance, and operational efficiency.
The CTC model validates e-invoices in real time before they are shared with buyers. Invoices that are approved are assigned a Unique Identifier (UUID) along with a QR code. The procedure enhances accuracy and transparency in tax reporting.
A UUID is a unique code assigned to every validated e-invoice by the LHDN platform. It confirms the invoice's authenticity, ensuring it cannot be duplicated or altered. UUIDs allow easy tracking of invoices, supporting transparency and compliance.
A QR code is generated after an invoice is validated through the Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri (LHDN) platform. It allows buyers, sellers, and tax authorities to verify invoice details for accuracy quickly. For B2C transactions, QR codes ensure compliance without requiring the buyer's full validation.
While a specific digital signature is not universally mandatory for all e-invoices in Malaysia, robust authentication and validation processes are required. The LHDN emphasizes secure transmission and data integrity. Specific industries or transaction types may have additional requirements. The overall system of validation by the LHDN, serves as a form of electronic authentication.
A Credit Note is generated when the value of an already issued invoice is reduced. It is typically used for returns, incorrect invoicing, or discounts after completing the sale. Credit Notes must be validated through the MyInvois platform like standard invoices.
A Debit Note is used to indicate an increase in the amount originally billed in an invoice. Debit Notes must also pass through Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri (LHDN) validation to ensure compliance. They furnish clarity and proper reporting of invoice revisions.
A Self-Billed Invoice is generated by a buyer on behalf of a supplier in specific contractual arrangements. These invoices must comply with Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri (LHDN) guidelines and undergo validation like regular invoices. Self-billing ensures accurate reporting and streamlines business processes.
Yes, businesses must issue export e-invoices for international goods or services sales. These invoices ensure accurate tax reporting, customs compliance, and proper documentation for cross-border trade. Export e-invoices follow the same validation process through LHDN.
The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN) is responsible for overseeing and implementing the e-invoicing mandate in Malaysia. It verifies e-invoices in real time to ensure accurate tax reporting and compliance. LHDN also provides technical guidelines and tools like the MyInvois platform and SDK.
