In today's fast-paced global business world, companies face challenges when exchanging essential documents securely and efficiently. Imagine a multinational business trying to work through different standards, systems, and rules in various countries.
PEPPOL Invoice, facilitated by the Pan-European Public Procurement Online network, began as a solution for invoicing public sector clients in Europe. Over time, PEPPOL Invoices have evolved into a global framework for secure, seamless electronic document exchange, connecting businesses and public entities worldwide in a unified, highly secure system. Countries like Malaysia are also leveraging PEPPOL e-Invoicing to drive digital transformation
Today, PEPPOL e-invoicing extends beyond Europe, with adoption in countries like Canada, New Zealand, Singapore, and the United States. With hundreds of thousands of public and private organizations registered, PEPPOL-based e-invoicing has become a key driver of efficient global electronic transactions, simplifying processes and reducing errors.
The future of PEPPOL-based e-invoicing lies in becoming a universal standard for electronic transactions. By standardizing formats and ensuring secure, cross-border communication, PEPPOL-based e-invoicing promises to revolutionize global business connectivity and streamline international operations.
What Challenges Do Businesses Face with PEPPOL Invoice?
While PEPPOL Invoice offer numerous benefits, businesses face challenges during implementation. Integrating PEPPOL with existing ERP systems can be complex and resource-intensive, especially for smaller companies. Navigating varying compliance requirements across countries adds to the difficulty.
In Malaysia, for instance, businesses must align their invoicing processes with Malaysia’s e-Invoicing Compliance Guidelines, addressing format and integration requirements (Malaysia E-Invoicing Compliance: Know Checklist & Challenges).
Maintaining data accuracy and security is another hurdle, as errors in invoice formats or missing information can disrupt transactions. Ensuring compliance with PEPPOL's strict security standards requires robust measures. Overcoming these challenges involves investing in reliable software, training, and expert support.
How Can Businesses Overcome Common PEPPOL Challenges?

Overcoming PEPPOL challenges requires strategic planning, reliable partnerships, and the right tools. Here's how companies can address key hurdles effectively.
- Streamlining Onboarding: Connecting to PEPPOL can seem complex, especially with technical and compliance requirements. Working with a certified Access Point provider simplifies the setup, ensuring compliance while easing the onboarding process. Many businesses in Malaysia rely on AP Automation solutions to make this process smoother
- Handling Compliance Variations: Different countries may have unique document standards, creating confusion. Regularly consulting with Access Point providers helps businesses stay compliant across borders by ensuring all document formats meet each country's standards.
- Integrating with Current Systems: Integrating PEPPOL with existing systems may require adjustments. Businesses can consult IT specialists or rely on support from Access Point providers to ensure seamless integration with minimal disruption. In Malaysia, companies often leverage the MYInvois Platform for integration
- Ensuring Data Security: Data security is crucial in electronic exchanges. Choosing Access Point providers with high-security standards, like encryption, helps safeguard sensitive data and ensure secure transmission.
- Managing Costs: PEPPOL-related expenses can be a concern for smaller businesses. Opting for scalable solutions and exploring provider plans that fit document volumes can help control costs while meeting operational needs.
- Training Staff Efficiently: Adapting to PEPPOL may require some employee training. Access Point providers often offer resources to help teams quickly learn the new processes, making the transition smoother and more efficient.
What Do You Need to Know About PEPPOL Invoice?
Multiple nations have traditionally operated e-invoicing systems—such as Sweden's Svefaktura, Norway's EHF, and Denmark's NemHandel. You may be familiar with these formats if your business has worked with public sector clients. However, as of April 18, 2020, all public sector organizations in the EU must now accept invoices in the standardized Universal Business Language (UBL) format through PEPPOL.
The PEPPOL invoice format, based on PEPPOL BIS Billing 3.0, uses the PEPPOL UBL invoice example as its standard for ensuring interoperability and compliance across countries.
While some countries still allow using their national e-invoicing standards, these gradually favor PEPPOL. Embracing the PEPPOL-based e-invoicing standard can simplify invoicing and improve efficiency, especially for businesses.
Beyond invoices, PEPPOL also supports exchanging a wide range of business documents, such as purchase orders, order confirmations, product catalogs, and shipping information. PEPPOL offers a secure, versatile solution that extends well beyond basic invoicing.
PEPPOL Invoice: What Are Their Key Objectives?
PEPPOL invoices aim to simplify and standardize electronic transactions globally, fostering greater efficiency, transparency, and accessibility. By addressing challenges in document exchange, PEPPOL helps businesses streamline operations and stay competitive in a rapidly digitalizing world.
For Malaysia, adopting PEPPOL-based e-Invoicing aligns with the nation's Continuous Transaction Control (CTC) model which promotes automation and compliance.
Easing Global Transactions and Enhancing Transparency
PEPPOL works to reduce the complexity businesses face when dealing with multiple systems across countries. Establishing a unified standard enables smoother and more transparent international transactions, helping to cut costs and streamline operations.
Encouraging Automation for Greater Efficiency
A primary goal of PEPPOL is to advance automation across both public and private sectors. This effort reduces manual tasks, increases accuracy, and allows businesses to improve their workflows more straightforwardly and efficiently.
Empowering SMEs to Compete Internationally
PEPPOL's standardized framework supports small and medium-sized enterprises by simplifying compliance with global regulations. This approach enables these businesses to adopt modern technologies and effectively position themselves in the worldwide market, boosting their competitive edge.
How Does PEPPOL Infrastructure Ensure Secure Business Connections?
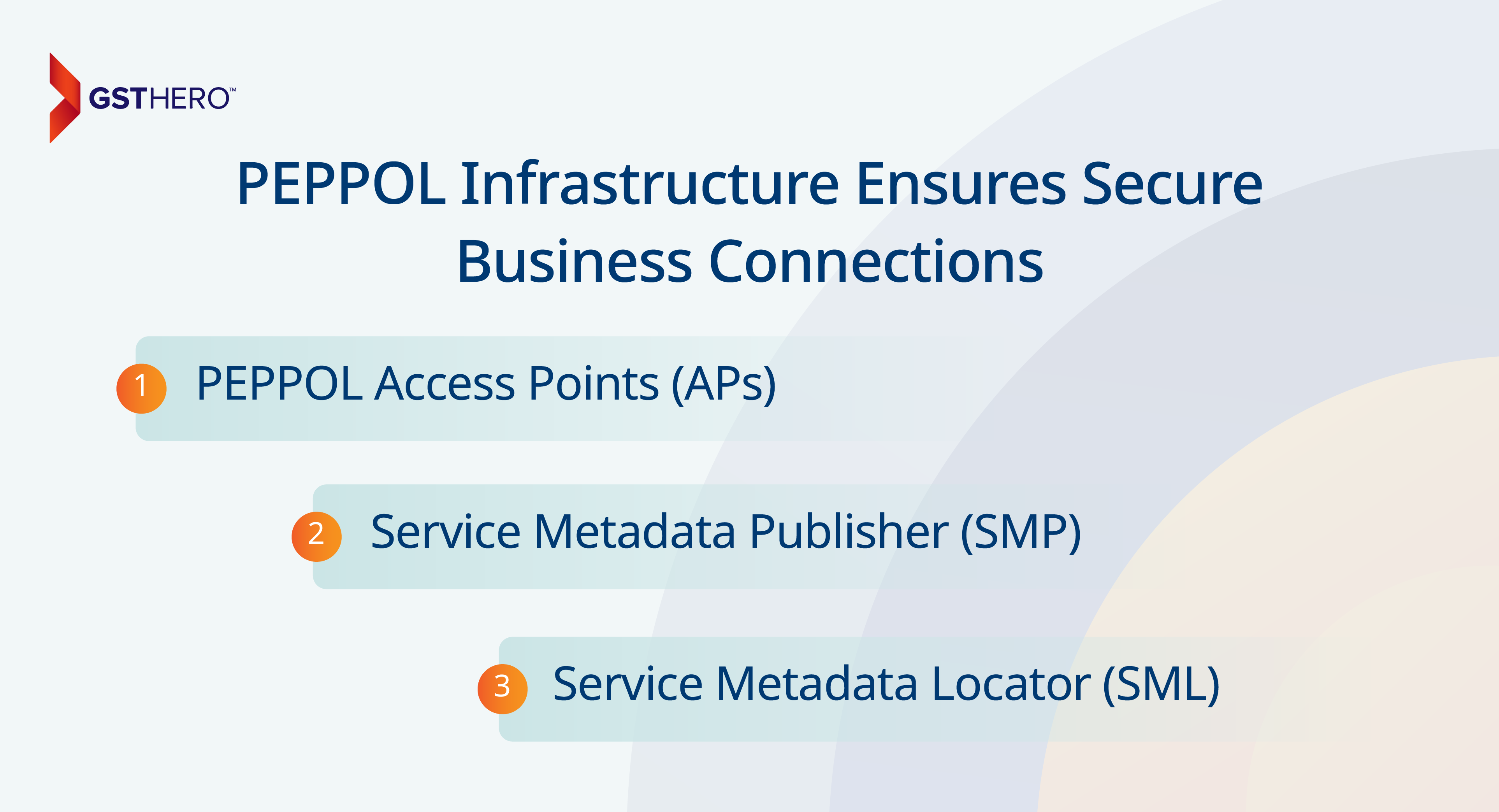
PEPPOL infrastructure has robust components that ensure secure and seamless document exchange. Each element works together to maintain compliance and data integrity, from certified Access Points to decentralized registries.
- PEPPOL Access Points (APs):
- Act as certified gateways in the PEPPOL network, linking participants securely.
- It is governed by PEPPOL's standards and protocols to ensure compliance.
- Each transaction flows from one Access Point to another, maintaining secure and standardized communication throughout the PEPPOL network.
- Service Metadata Publisher (SMP):
- The Service Metadata Publisher is a decentralized registry that provides crucial information about Access Points and the types of messages a recipient can process.
- It stores user addresses and metadata, facilitating efficient routing of documents within the PEPPOL Network.
- Every participant is assigned a unique PEPPOL ID (formatted as a URL), which links to the correct Service Metadata Publisher, ensuring seamless and accurate document exchange.
- Service Metadata Locator (SML):
- The Service Metadata Locator acts as a central directory, linking each participant to their respective Service Metadata Publisher (SMP), streamlining the identification and routing process.
- It maintains a unique identifier for every partner, enabling Access Points to locate the correct Service Metadata Publisher and the recipient's Access Point efficiently.
- By integrating these components, the Service Metadata Locator ensures smooth, secure, and accurate document exchange between businesses on a global scale.
Each participant can be identified through the PEPPOL Directory, which facilitates easy discovery of registered users within the PEPPOL e-invoicing network.
What Are the PEPPOL 4-Corner and 5-Corner Models?
The 4-Corner Model
The 4-corner model is the foundation of PEPPOL's electronic document exchange, linking four key participants: the sender, the recipient, and their separate Access Points. This model allows both parties to be anywhere worldwide as long as they are registered within the PEPPOL network.
Here's the process:
- The sender forms an electronic document, such as an invoice, and transmits it to their assigned PEPPOL Access Point.
- The sender's Access Point securely links with the recipient's Access Point and transmits the record.
- The recipient's Access Point then delivers the document to the recipient's internal system, completing the exchange.
This framework enables businesses worldwide to securely exchange documents, simplifying cross-border transactions and creating a standardized communication method.
The 5-Corner Model: PEPPOL CTC
The 5-corner model, called Continuous Transaction Control (CTC), extends the 4-corner model by introducing a government platform as a fifth participant. This additional component allows tax authorities to receive accurate or near real-time transaction data, including critical details like the Tax Registration Number (TRN), enhancing tax oversight and ensuring compliance.
Here's how it works:
- The document exchange process follows a similar structure to the 4-corner model. However, once the recipient's Access Point receives the document, it forwards a copy to the central government platform, ensuring the inclusion of the Tax Registration Number (TRN).
- This process enables tax authorities to monitor transaction details as they occur, gaining accurate insights into business activity and verifying compliance through the Tax Registration Number (TRN) and other essential data.
The 5-corner model combines regulatory oversight with business efficiency, offering a secure, adaptable framework that meets compliance and operational needs. Through PEPPOL's decentralized approach, businesses benefit from a streamlined document exchange system that respects global standards and local regulatory requirements.
What Is the Role of a PEPPOL Authority?
Businesses must utilize Access Points to connect to the PEPPOL network for secure electronic document exchange. These Access Points function under the supervision of PEPPOL Authorities, ensuring they adhere to strict technical standards and provide reliable services.
Currently, 17 PEPPOL Authorities worldwide oversee the PEPPOL network, verifying that Access Points comply with established security and technical requirements. Businesses using the PEPPOL network can trust the reliability and security of their electronic transactions.
In addition to oversight, PEPPOL Authorities set country-specific guidelines for document formats and content tailored to local business needs. Utilizing the Universal Business Language (UBL), these standards help businesses meet compliance requirements while maintaining compatibility with the broader PEPPOL framework.
PEPPOL Authorities work closely with OpenPEPPOL, the non-profit organization responsible for developing and expanding PEPPOL standards.
Is using PEPPOL mandatory for electronic invoice and document exchange?
From April 2020, all public sector bodies within the EU have been required to accept and process e-invoices through the PEPPOL network. This mandate was established to simplify and standardize public procurement processes, enabling companies to conduct domestic and cross-border B2G (business-to-government) transactions without navigating differing national requirements.
Across the EU, many countries have adopted PEPPOL-based e-invoicing as their primary framework, with some even mandating its use for B2G invoicing.
Beyond Europe, countries like Singapore, Australia, and New Zealand have also started implementing PEPPOL, marking a global shift toward streamlined and secure PEPPOL-based e-invoicing practices.
How Does PEPPOL Work? A Simple Breakdown
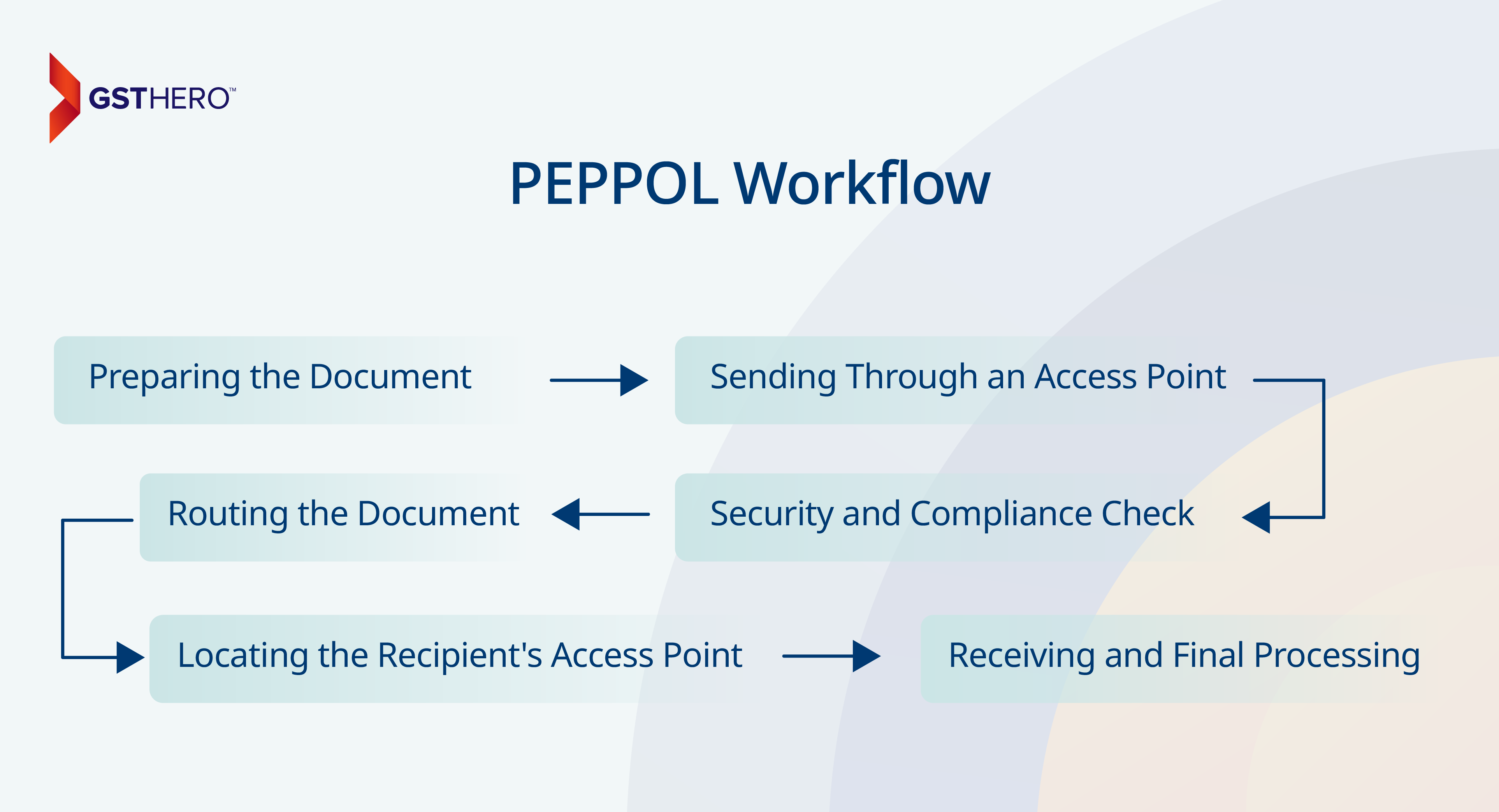
PEPPOL simplifies electronic document exchange by ensuring a secure and standardized process for businesses and governments. Here's a step-by-step overview of how a document, like an invoice, moves seamlessly through the PEPPOL network.
Preparing the Document
The sender creates an electronic document, like an invoice, using PEPPOL-compliant software. Ensures that the document's format meets PEPPOL's requirements.
Sending Through an Access Point
The document is sent through a certified PEPPOL Access Point, a secure gateway for transmitting documents across the network.
Security and Compliance Check
The Access Point verifies the document to ensure it meets PEPPOL's security and formatting standards.
Routing the Document
The Access Point retrieves the recipient's details using the Service Metadata Publisher (SMP), which stores information about the recipient's Access Point and accepts document types.
Locating the Recipient's Access Point
The Service Metadata Locator (SML) acts as a central directory, directing the document to the recipient's Access Point based on their unique PEPPOL ID.
Receiving and Final Processing
The recipient's Access Point receives the document, verifies it, and forwards it in a compatible format to the recipient, where it can be processed securely and efficiently.
How GSTHero Simplifies PEPPOL Integration and Compliance
GSTHero, a leading compliance software provider, offers businesses a seamless way to integrate with the PEPPOL network and efficiently manage their electronic invoicing needs.
Designed to simplify GST compliance and automate processes, GSTHero's solutions ensure businesses remain compliant with PEPPOL standards while streamlining their document exchange workflows.
GSTHero helps businesses overcome integration challenges, maintain data accuracy, and adhere to local and international compliance requirements by providing end-to-end support, from secure invoice generation to automated validation and routing.
With its user-friendly interface and robust security measures, GSTHero empowers businesses to leverage the benefits of PEPPOL, making cross-border transactions effortless and enhancing operational efficiency.
Conclusion
PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement Online) is changing how businesses and governments exchange documents by making electronic transactions more straightforward, secure, and easier to manage across borders.
PEPPOL-based e-invoicing removes the need to navigate multiple national e-invoicing standards, reducing costs and making compliance easier. With support from PEPPOL Authorities to maintain quality and ensure local alignment and guidance from OpenPEPPOL to keep the system up-to-date and expanding, PEPPOL-based e-invoicing is becoming a valuable tool for businesses worldwide.
As more companies adopt it, PEPPOL, utilizing the Universal Business Language, is not just a solution for today's needs but a pathway to smoother international business and more efficient operations in the future.
