By planning the well-organized introduction of e-invoicing, Malaysia has put itself among the many highly compliant countries in the world. However, this is not an uncommon event. The rise of e-invoice implementation has increased quite significantly in the last few years.
More and more countries are recognizing the legal, financial, and operational benefits of making e-invoicing mandatory. It has made electronic invoicing a standard practice in several leading countries like the USA, Australia, India, Spain, and France.
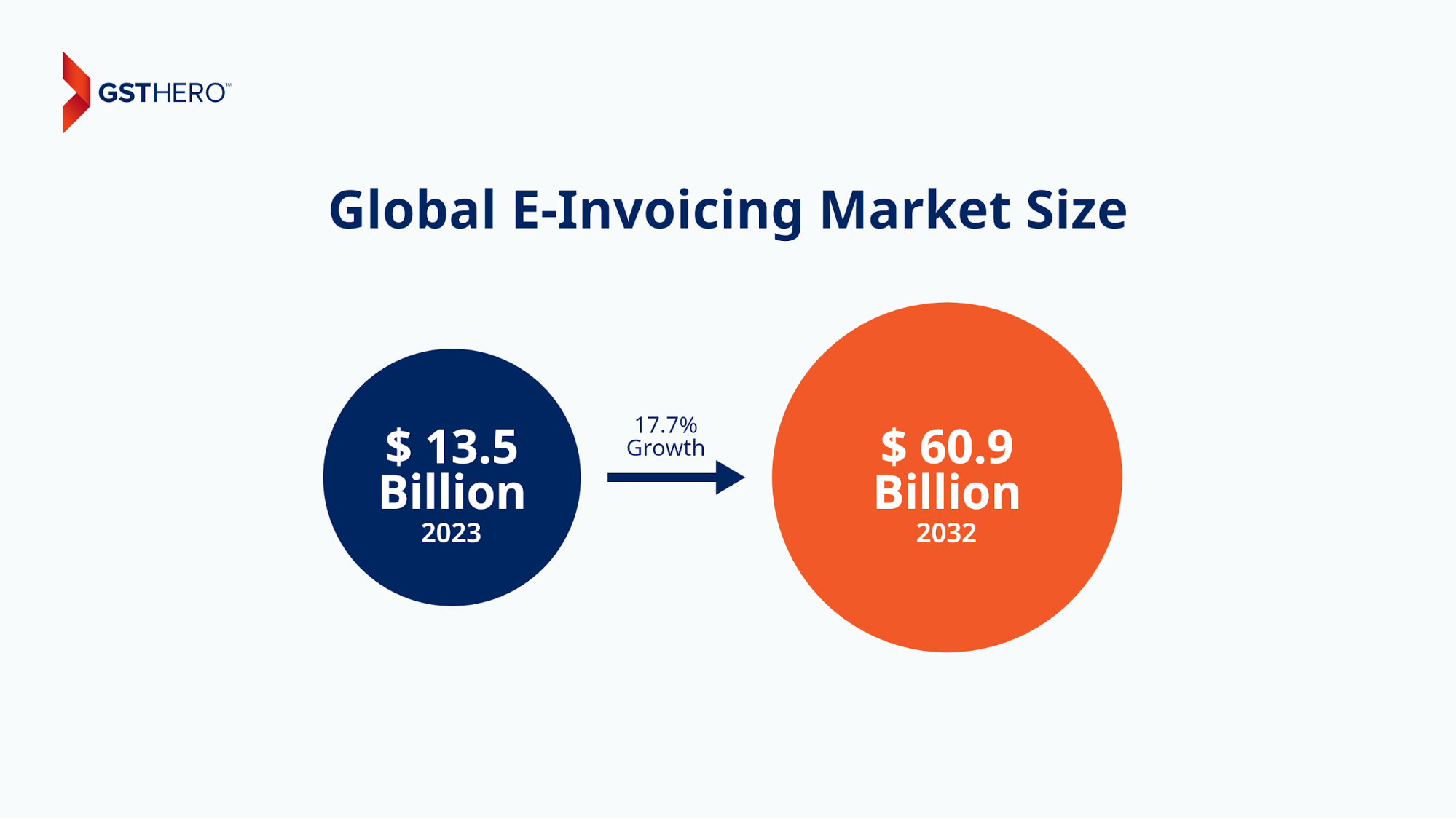
As a result, the global e-invoicing market size has reached 13.5 billion USD in 2023, with an estimation that it will grow by 17.7%, and reach 60.9 billion USD by 2032.
The IRBM has decided to become a part of such a rapidly growing industry by revitalizing the tax administration management in Malaysia.
This move will help them reap e-invoicing benefits like-
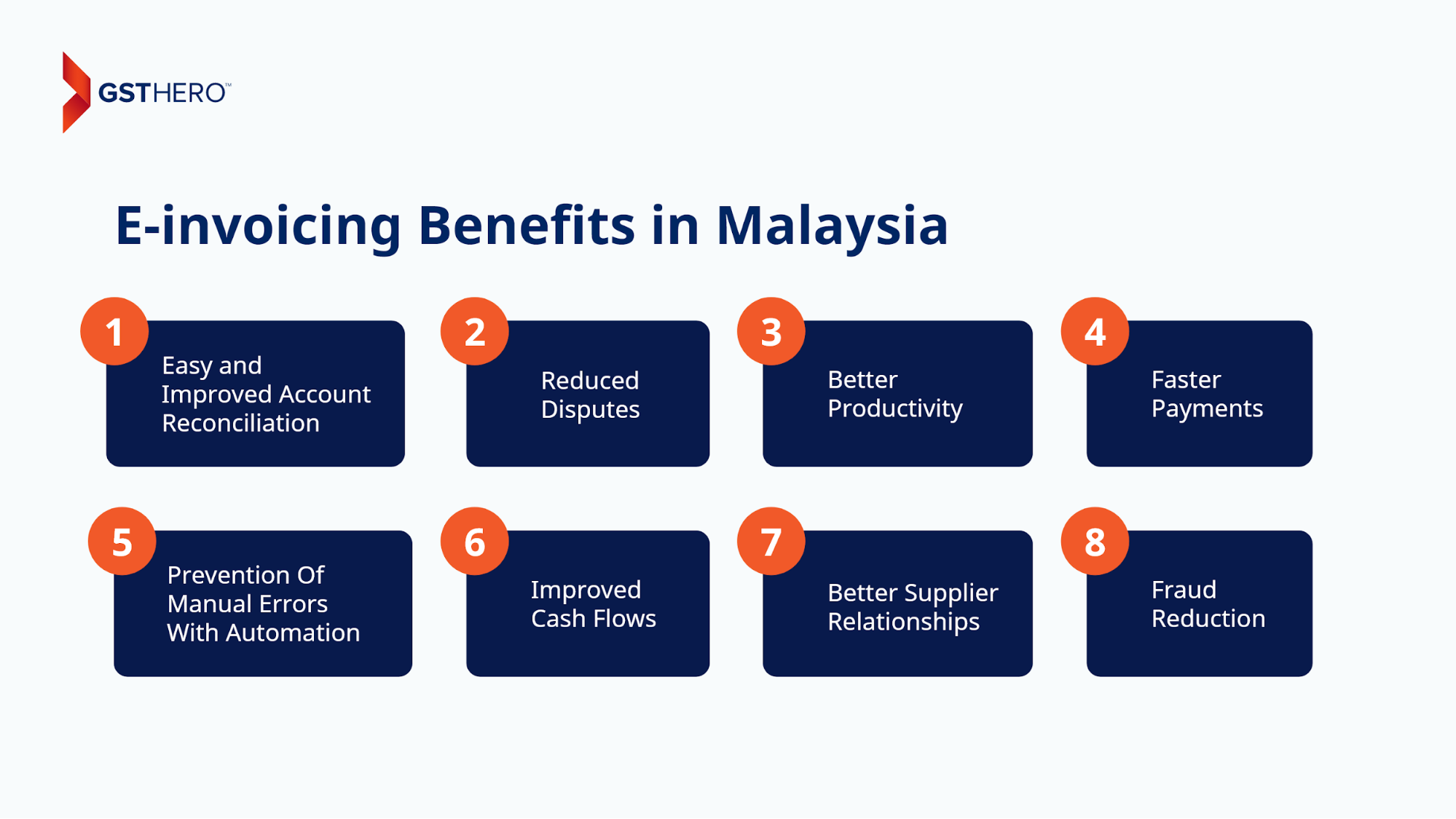
- Easy and Improved Account Reconciliation
- Reduced Disputes
- Better Productivity
- Prevention Of Manual Errors With Automation
- Faster Payments
- Improved Cash Flows
- Better Supplier Relationships
- Fraud Reduction
What is E-Invoicing in Malaysia?
An electronic invoice or e-invoice is a document that is electronically exchanged between a supplier and a buyer through specialized e-invoice software. In Malaysia, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) specifies the electronic invoice format.
A valid invoice in Malaysia will contain 53 e-invoice mandatory fields, including seller & buyer details, item description, quantity, price, tax, total amount, payment details, etc.These fields are grouped into 9 categories :
- Address
- Business Details
- Contact Number
- Invoice Details
- Parties
- Party Details
- Payment Info
- Products / Services
- Unique ID Number
Also, the Malaysian government will use a Continuous Transaction Control (CTC) model for verifying sales invoices via the government’s API.
A Tax Identification Number (TIN) introduced in 2022 will power the use of e-invoicing in Malaysia.
Once validated and approved by the Inland Revenue Board (IRB), a serial number will be shared with the supplier via email. With this approach, the Malaysian government aims to adopt a CTC system connected to the Peppol network.
Such an invoicing process prevents the necessity of a traditional paper-based method by incorporating a much faster and more secure system of transfer.
Some Key Benefits :
- Due to the electronic medium, e-invoices are ready for use instantly after the completion of the required documentation.
- Any authorized party can access this documentation as it is stored on a centralized e-invoicing platform, offering greater ease of access compared to manual methods.
- Automation will be the core advantage of implementing e-invoicing In Malaysia, reducing processing time and the risk of errors.
E-Invoicing in Malaysia - Beginning
Malaysia’s tax office, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM), made the decision to mandate e-invoicing in March 2023 with a phase-wise implementation plan.
The goal of the Ministry of Finance with this move was to digitize and streamline tax administration operations in Malaysia.
The Malaysian government aimed to ensure the various benefits of e-invoicing for the country, such as :
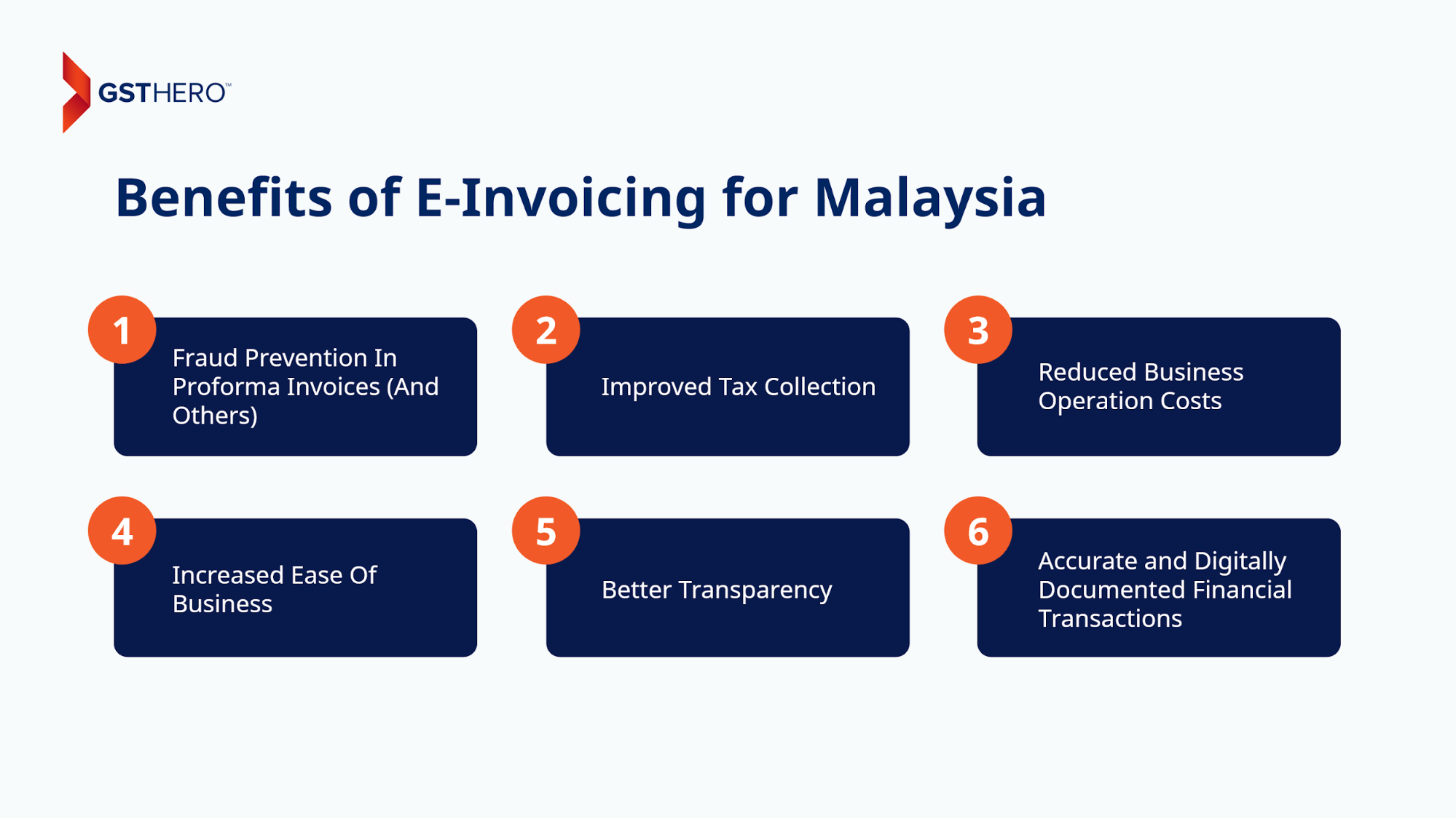
- Fraud Prevention In Proforma Invoices (And Others)
- Improved Tax Collection
- Reduced Business Operation Costs
- Increased Ease Of Business
- Better Transparency
- Accurate and Digitally Documented Financial Transactions
However, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) postponed the e-invoice implementation date in October 2023, giving businesses time to understand and adopt the concept of e-invoicing into their operations.
As of now, the Malaysian Tax Authority, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia/Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri Malaysia (LHDN), and the Malaysian Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC) plan to implement the electronic invoicing regulations by August 2024.
Once implemented, the e-invoicing practice will be mandatory for B2B, B2C, and B2G transactions, both domestic and international. This move will not only improve tax administration in Malaysia but also provide several tech-driven + automation benefits.
E-Invoicing Implementation Timeline in Malaysia
To make the transition easier and smoother for all small, medium, and large businesses, the IRBM, MDEC, and Malaysian government are using a phase-wise approach to implement e-invoicing and its regulations.
Starting from 1st August 2024, the implementation of e-invoice in Malaysia is scheduled to be completed within 2 to 3 years, with 1 July 2025 determined as the estimated final date for implementation.
Refer to the table below to understand the timeline:
Sr. No | Date | Implementation Plan |
1 | 1st August 2024 | Largest Taxpayers - E-invoicing will be in effect for taxpayers with an annual revenue/turnover of more than RM 100 million. |
2 | 1st January 2025 | Standard Taxpayers - E-invoicing will be in effect for taxpayers with an annual revenue/turnover of more than RM 25 million and within RM 100 million. |
3 | 1st July 2025 | All Taxpayers - E-invoicing will be in effect for all taxpayers (small, medium, or large). The specific size of the turnover for e-invoicing will not be a relevant factor after this implementation. |
The Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri Malaysia/Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia has determined this phase-wise e-invoicing implementation timeline to help taxpayers better prepare and plan the transition to e-invoicing before the final date.
E-invoicing Authority in Malaysia
The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) holds regulatory authority over e-invoicing endeavors in the country.
Luckily, the IRBM/Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri Malaysia has taken a proactive approach towards incorporating and solidifying e-invoicing in the country by creating a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the Malaysian Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC).
This unified effort between the IRBM and MEDC will promote a smoother transition to e-invoicing and its success in the country.
In July 2023, IRBM also introduced a comprehensive e-invoicing Malaysia Guideline, outlining a meticulous framework for its adoption across diverse sectors.
The Key Components of E-invoicing In Malaysia
It is a good idea to understand what will go into e-invoices in Malaysia before implementing it, so let’s look into it.
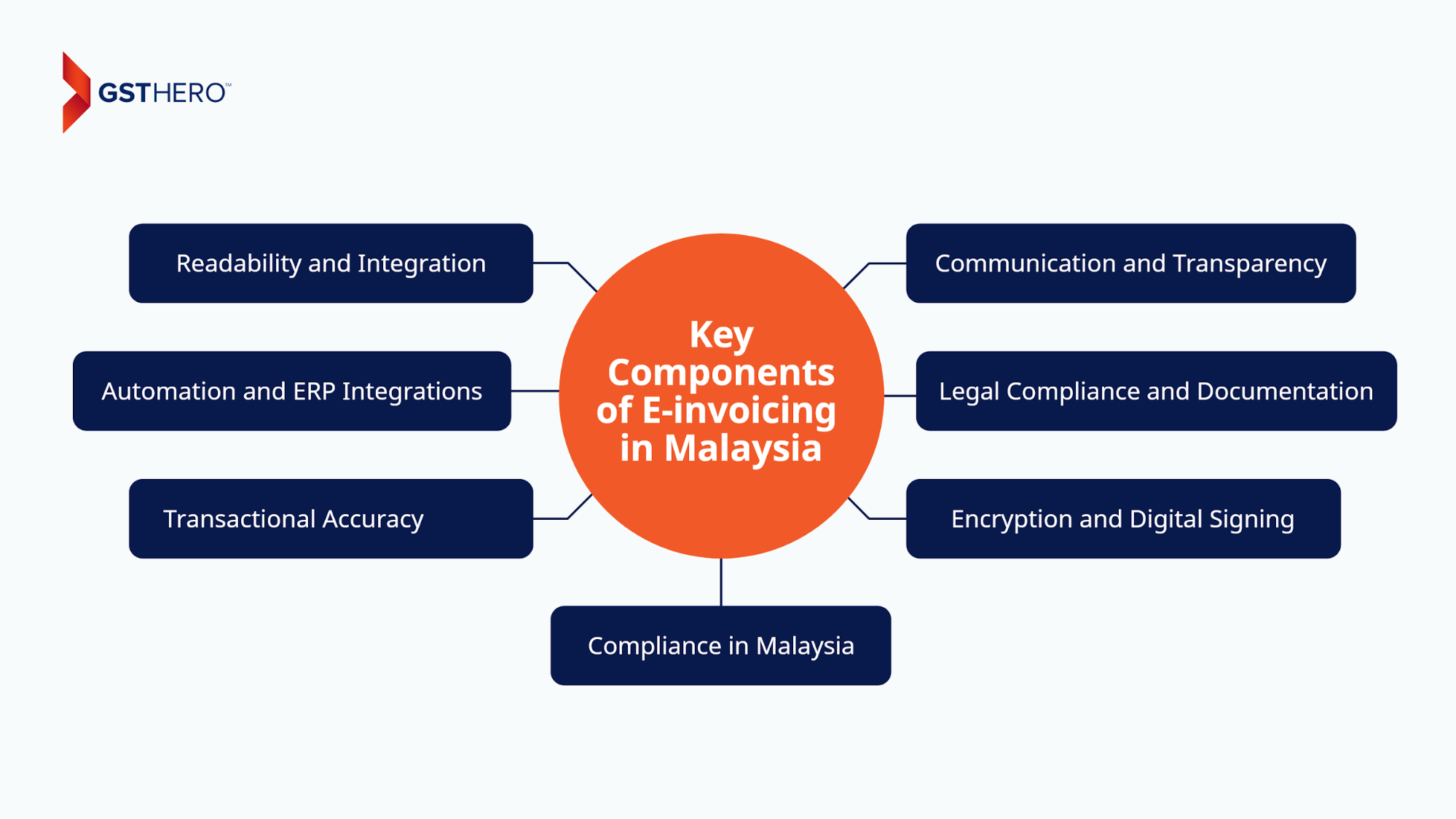
- Readability and Integration
As e-invoices use well-organized formats like JSON or XML, they offer better readability and integration with a wide range of business systems. - Automation and ERP Integrations
Automation in e-invoicing prevents manual errors and streamlines processes, offering secure integration with multiple ERPs for faster invoice generation, transfer, and processing. - Transactional Accuracy
E-invoices contain essential data such as invoice number, date, line item details, payment terms, and party information. Standardizing this data is highly recommended for interoperability among different systems. - Compliance in Malaysia
Adhering to Malaysian regulations regarding e-invoicing formats, authenticity, archiving, and data retention is imperative to facilitate transactions, avoid legal issues, and meet compliance standards. - Encryption and Digital Signing
E-invoicing in Malaysia will require better authentication protocols with encryption and digital signature for secure transmission, preventing unauthorized access and illegal tampering. - Legal Compliance and Documentation
Using E-invoice archiving software to maintain audit trails is crucial for legal compliance and proper documentation. It enables data backups, better transparency in transactions, and faster dispute resolutions. - Communication and Transparency
It is necessary to utilize a 1-click portal for buyer and supplier e-invoices to ensure better communication, invoicing status tracking, transparency, and dispute resolutions. It enables faster invoice generation, submission, and review by buyers.
Overall, embracing e-invoicing in Malaysia with the right strategy will offer efficiency, security, and compliance benefits for businesses.
Quick Note: Compliance's meaning in Malay is Pematuhan.
Scenarios For Which E-invoice Must Be Issued :
Below you will learn about scenarios for which issuing e-invoices will be mandatory as specified by Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri Malaysia.
Proof of Income
Issuance of e-invoices is mandatory when your business supplies goods or services to a recipient, enabling accurate tracking of sales and revenue by the government. Additionally, documenting "other transactions" involving earnings may also be necessary, although specific guidelines for such transactions have not been issued by the IRBM/Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri Malaysia as of yet.
Proof of Expenses
E-invoices are essential for documenting purchases, expenses, returns, or discounts. When someone buys a product or service from your business, it's imperative to issue an E-invoice to them. It ensures accurate record-keeping of the expenses incurred by the taxpayer. This includes any discounts provided to consumers.
Additionally, if the transaction involves a Malaysian recipient and a foreign seller, the recipient must issue a self-billed invoice to document the expense. Keeping backups of this documentation is vital, as the Malaysian tax department could request it.
Types of E-invoices in Malaysia
Malaysia’s e-invoice system will include and mandate the issuance of the following documents for its “e-invoicing Malaysia LHDN” initiative :
Invoices
Invoices are used to document the sales transactions between suppliers and buyers, including self-billed invoices for tracking expenses. They are used to document the product/services offered, the pending amount, and payment terms/conditions.
Here’s one example of an SST invoice format - Malaysian government-approved.Credit Notes
Credit notes are documents issued by sellers to rectify or modify the value of previously issued e-invoices without necessitating a refund to the buyer. These adjustments may arise from errors, application of discounts, or product returns, ensuring accurate reflection and accounting of any changes to transaction values.
Specifically, they act as corrective measures for discrepancies in the original transaction value, addressing errors in the invoice, discounts, or returns of goods or services. They serve to reduce the value of the original invoice without requiring a refund to the buyer.
Credit notes are exclusively utilized in cases where there's a decrease in transaction value, typically due to errors in invoicing, but they are not used for refund scenarios.
Here’s one example of a credit note sample - Malaysian government-approved.Debit Notes
Debit notes are supplementary documents issued by sellers to maximize the total amount of a previously issued e-invoice, reflecting an increase in the transaction value. This adjustment typically arises from additional costs or charges not initially included in the original invoice.
Unlike credit notes, which address discrepancies by reducing the transaction value, debit notes are utilized to record additional costs associated with previously issued e-invoices. They provide clarity on the initial transaction and enable sellers to request supplementary payment from buyers for post-billing expenses.
In short, debit notes are issued in cases of increased transaction value, contrasting with credit notes, which are issued for decreased transaction values.
Refund Notes
Refund notes, also known as refund e-invoices, are official documents issued by sellers to confirm the refund of the buyer's payment, thereby completing the transaction cycle. These invoices play a crucial role in maintaining accurate financial records and facilitating audits.
They are essential whenever money is refunded, ensuring both parties have a record of transaction reversals or adjustments.
Note:
Each e-invoice will bear a unique identifier number and undergo 51 validations, with 35 being mandatory.
Types of Transactions Covered Under Malaysia E-invoice
e-Invoicing in Malaysia applies to all commercial activities in the country including the sale of goods and services.
The official mandate by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia covers the following types of transactions :
Business-to-Business (B2B)
B2B invoicing through an electronic medium enables hassle-free payments, effortless invoicing, and better operational efficiency for all business-to-business transactions. A well-developed B2B invoicing software can help a business improve productivity and cash flows by automating multiple time-consuming and manual tasks.
The benefit from B2B e-invoicing is not a single one, but multidirectional, offering lucrative advantages at both the business and day-to-day operational level activities.Business-to-Customer (B2C)
E-invoicing for B2C business transactions helps simplify invoicing for businesses regularly dealing with individual customers. However, sellers are not obligated to issue e-invoices to customers in the B2C scenario. They can provide a traditional invoice or receipt as well.
Be that as it may, after a certain period, sellers are required to aggregate all the issued invoices and receipts to generate a consolidated e-invoice.
Business-to-Government (B2G)
While the flow of e-invoicing in B2G is similar to that of B2B, it offers the benefits of e-invoicing for transactions between businesses and government establishments / organizations.
Important :
E-invoicing in Malaysia applies to all taxpayers/individuals/legal entities conducting a commercial activity, including but not limited to :
- Association
- Body of Persons
- Branch
- Business Trust
- Co-Operative Societies
- Corporations
- Limited Liability Partnership
- Partnership
- Property Trust Fund
- Property Trust
- Real Estate Investment Trust
- Representative Office and Regional Office
- Trust Body
- Unit Trust
E-Invoicing Methods in Malaysia
Depending on the requirements of a business such as volume and customization, there are 3 invoicing methods in Malaysia to report/transmit tax invoices to the IRBM.
- The MyInvois Portal
- Application Programming Interface (API)
- Peppol Service Providers
Let’s look into MyInvoisPortal Vs. API for e-invoicing Malaysia :
The MyInvois Portal
The MyInvois Portal is a web-based platform provided and hosted by IRBM/Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri Malaysia (LHDN). It is a free portal for uploading invoices and a perfect option when connecting to APIs for e-invoice is an obstacle. However, it is only suitable for small and medium-sized businesses since it can process limited volumes of data. Large enterprises with low invoice volume requirements might also find it useful.
This portal includes prepared templates for e-invoicing, preventing the need for additional tools or invoice software. Malaysia’s IRB has also made ERP integration with MyInvois possible and easy to do, making it a widely usable tool for taxpayers.
The MyInvois Portal is compatible with both Web and Mobile Interfaces.
To manually upload an invoice to MyInvois, follow these steps:
- Visit the MyInvois website and log in to your account.
- Click on the “Invoices” tab.
- Select “Add New Invoice”.
- Choose the “Manual Upload” option.
- Browse for the invoice file you wish to upload.
- Click the “Upload” button.
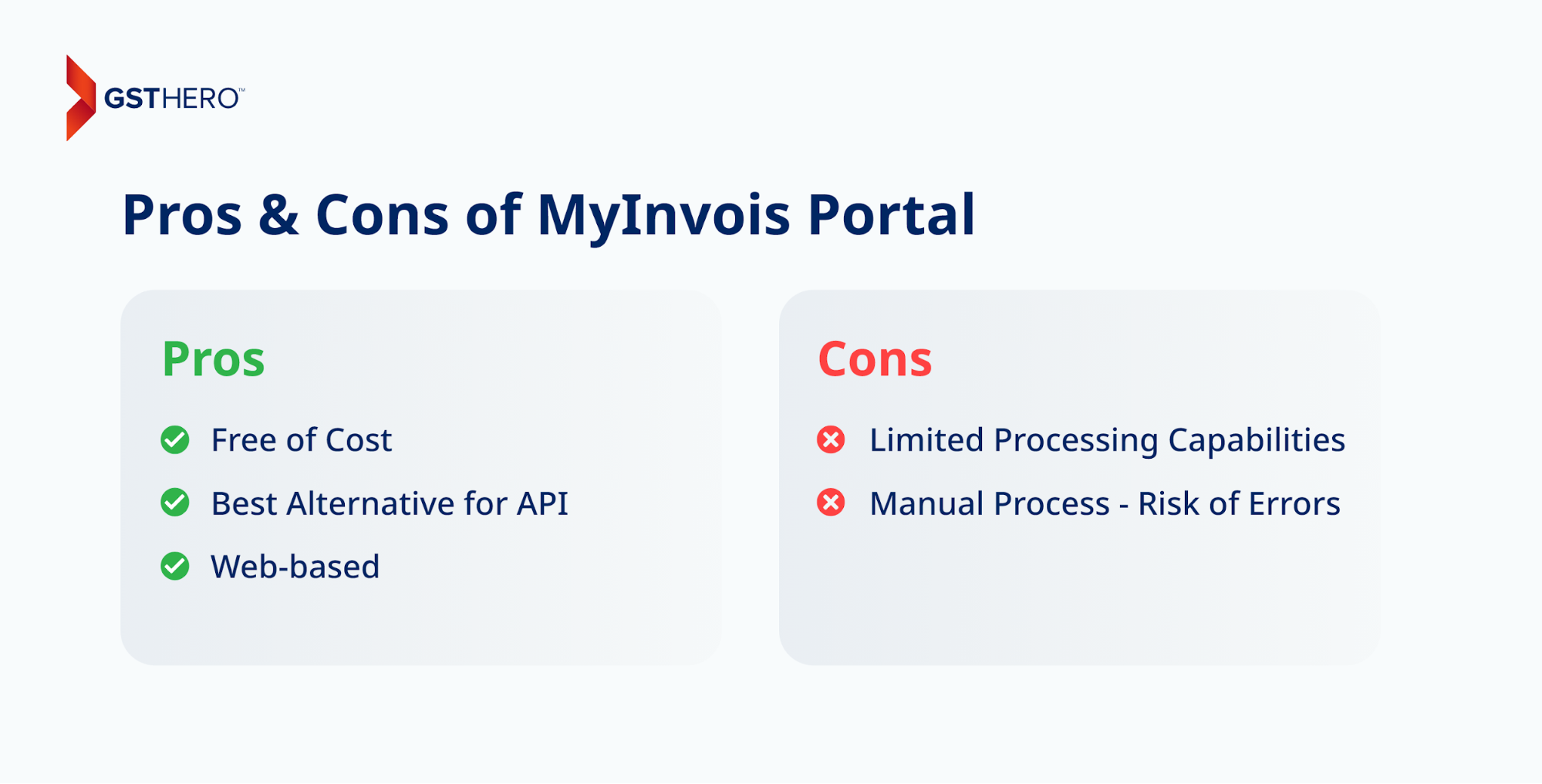
Pros of The MyInvois Portal
- Free of Cost
- Best Alternative for API
- Web-based
Cons of The MyInvois Portal
- Limited Processing Capabilities
- Manual Process - Risk of Errors
Application Programming Interface (API)
When the requirement includes large volumes of invoices, the API proves to be a more suitable option for e-invoice transmission. It allows direct transmission between the MyInvois System and the system used by taxpayers. API for e-invoicing in Malaysia is a great option for large enterprises with higher invoice volume and integration needs.
Customization and technology investment are required for using API in Extensible Markup Language (XML) or JavaScript Object Notation (JSON format).
With API Integration, taxpayers can generate e-invoices using their ERP systems in real time, and prevent the need for manual intervention when delivering them to the IRB database.
The API integration method offers the advantage of the real-time generation of e-invoices within the ERP system, directly delivering them to the IRB database.
Direct integration enables close to real-time synchronization of data between the ERP and the MyInvois portal, making these e-invoices instantly available for the validation and approval process.
With integration and automation, API methods offer better operational efficiency and customization to businesses in e-invoicing.
For example, a business can use an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system like SAP to integrate with the MyInvois portal for the transmission of invoices.
Pros of Application Programming Interface (API) for E-invoicing in Malaysia
- Automation to Prevent Manual Errors
- Wide Range of ERPs for Integration
- Better Efficiency
- Real-time and Accurate Invoice Generation + Delivery to the IRB
Cons of Application Programming Interface (API) for E-invoicing in Malaysia
- Requires investment in technology.
- Requires customization of existing systems.
- API Integration requires additional effort and expenses for compliance.
- ERP localization according to legal regulations can be a challenge.

Peppol Service Providers
Using API integration through a PEPPOL service provider, Malaysia’s and cross-border suppliers can transmit e-invoices to LHDNM. It would enable them to benefit from the interoperability facilitated by PEPPOL.
For API
During the E-invoice file validation process, three types of validation rules are implemented :
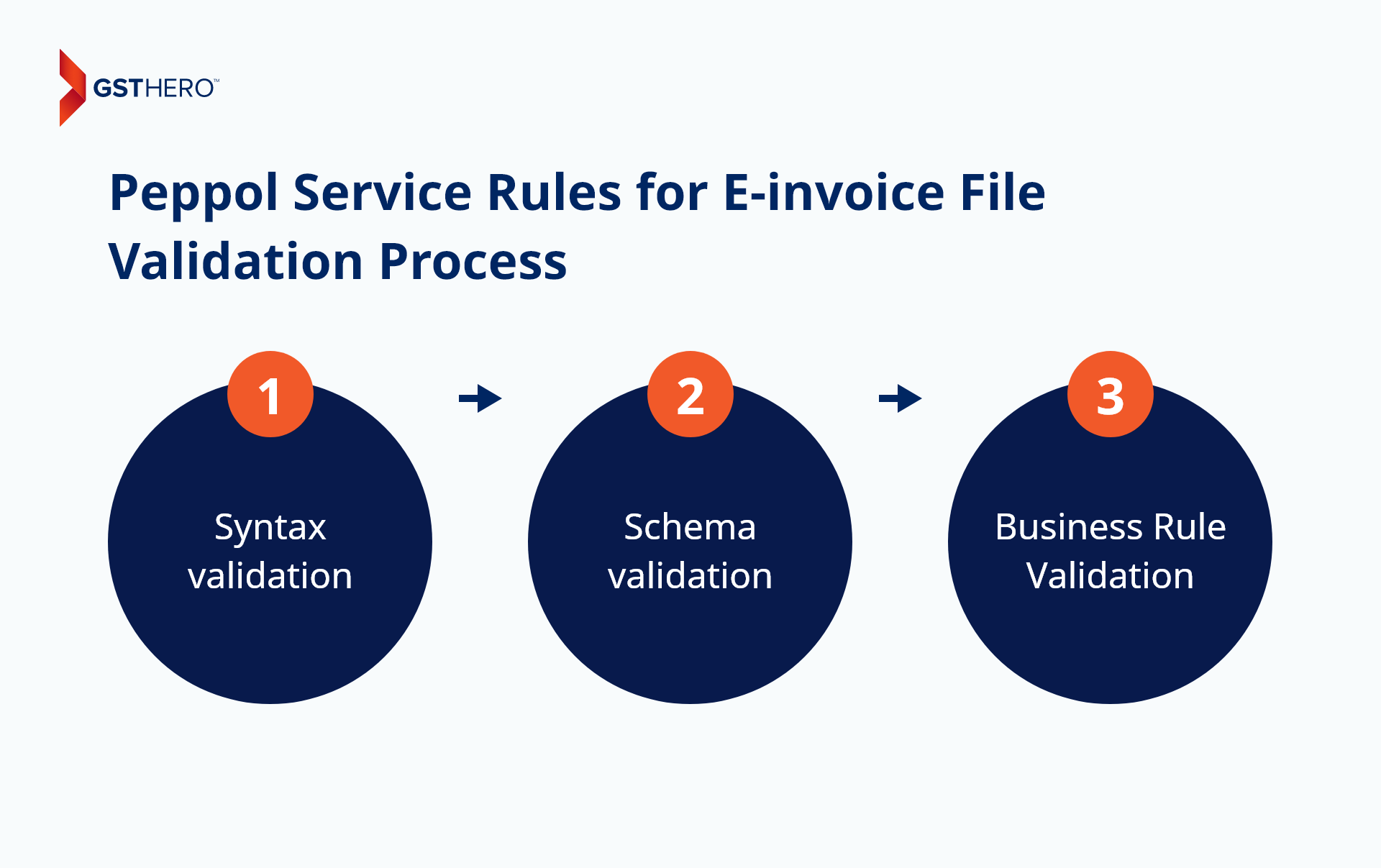
- Syntax validation
- Schema validation
- Business Rule Validation
These validations are crafted to manage text and character data according to the UTF-8-character encoding standard.
Following validation, buyers have a 72-hour window to request rejection, while taxpayers can request cancellation within 72 hours of receiving API notification.
What is the Goal Behind the “Malaysia e-Invoicing 2024” Initiative?
While there are many goals to achieve with e-invoicing, the primary and most important ones for the Malaysian government are digital transformation and automation in tax administration.
Below you will find more information on what the Malaysian government aims to achieve with e-invoice implementation:

Streamlined Tax Processes
Tax digitization through e-invoicing will help businesses save time, effort, and resources when managing tax processes. It will increase the ease of conducting operations and overall efficiency.
Information Security (InfoSec)
By preventing the need for paper-based invoicing, the Malaysian government aims to offer better security for invoices generated and exchanged by businesses through the MyInvois portal, avoiding leakages and tampering.
Accuracy and Transparency
With electronic invoicing powered by automation and strict validation protocols of IRBM, businesses can improve transparency and ensure better accuracy in their e-invoices while preventing errors.
Eco-Friendly - E-invoice LHDN Initiative
By transitioning to an electronic method, the Malaysian government also aims to reduce the negative impact on the environment caused by paper production and usage.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
With a digital portal and automation, the generation, validation, and approval of invoices will happen much faster and more effectively, making cash flow management easier for businesses.
Easy Compliance Process
With an IRBM-hosted portal like MyInvois, meeting compliance requirements, staying up to date with tax regulations, and preventing tax fraud will also be easier.
Globally Recognized Tax Compliance
Aligning with international best practices and standards for e-invoicing in tax management and reporting will improve Malaysia's reputation as a business-friendly destination. With digital invoicing, it will be possible to streamline international trade while facilitating documentation and operational efficiency in cross-border transactions.
Stable Revenue Growth
With increased transparency and accuracy, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia aims to prevent unnecessary revenue loss for businesses.
Real-time Visibility
The tax authority will be able to monitor and track all invoices in real time after digitization. It will make it possible to identify and deal with any discrepancies or potential tax evasions.
Cost Savings
Automation and digitization through e-invoicing will reduce the amount of resources and time required for manual administrative tasks.
e-Invoicing Process Flow in Malaysia
Below you can learn about the e-invoice workflow in Malaysia from the instant when the sale/transaction takes place and e-invoices are issued by supplier/vendor using MyInvois or API to the process of validation and storage of e-invoices on the IRBM’s database.
Generation of E-invoice
Once a sale or transaction takes place, the supplier will create e-invoices and share them for validation with the IRBM portal, using MyInvois or an API.
Validation of E-invoice
The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia will conduct validation of E-invoices in real time to verify compliance with the required criteria and standards.
After successful validation, the IRBM will send a unique identifier number (UIN) to the supplier via MyInvois or API, allowing them to have better traceability and prevent the risk of e-invoice tampering.
Notification of E-invoice Validation
Both the supplier and buyer will get a notification from the IRBM via MyInvois or API after the successful validation of the e-invoice.
Sharing of E-invoice
After e-invoice validation, the supplier is obligated to share with the buyer a validated e-invoice with an embedded QR code. This QR code generation helps verify the status and authenticity of the e-invoice through the MyInvois portal.
Rejection or Cancellation
In the event of errors in an e-invoice, the buyer has a window of 72 hours from the validation time via the MyInvois portal or Application Programming Interface (API) to request its rejection.
After the rejection request is sent with a specified reason, a notification is promptly dispatched to the supplier.
Recently clarified by the IRB, if the supplier acknowledges the reason provided by the buyer, they may proceed to cancel the e-invoice within the same 72-hour timeframe from validation.
However, if the supplier does not acknowledge the buyer's request or fails to withdraw the e-invoice within the specified time, cancellation will be prohibited after 72 hours. Any necessary modifications to the e-invoice would then require the issuance of a new e-invoice, such as a credit note or refund note e-invoice.
9 Benefits of e-Invoicing in Malaysia
The adoption of e-invoicing in Malaysia offers numerous benefits to businesses. It will help them improve their day-to-day operations and compliance with tax regulations.
Here are some key advantages :
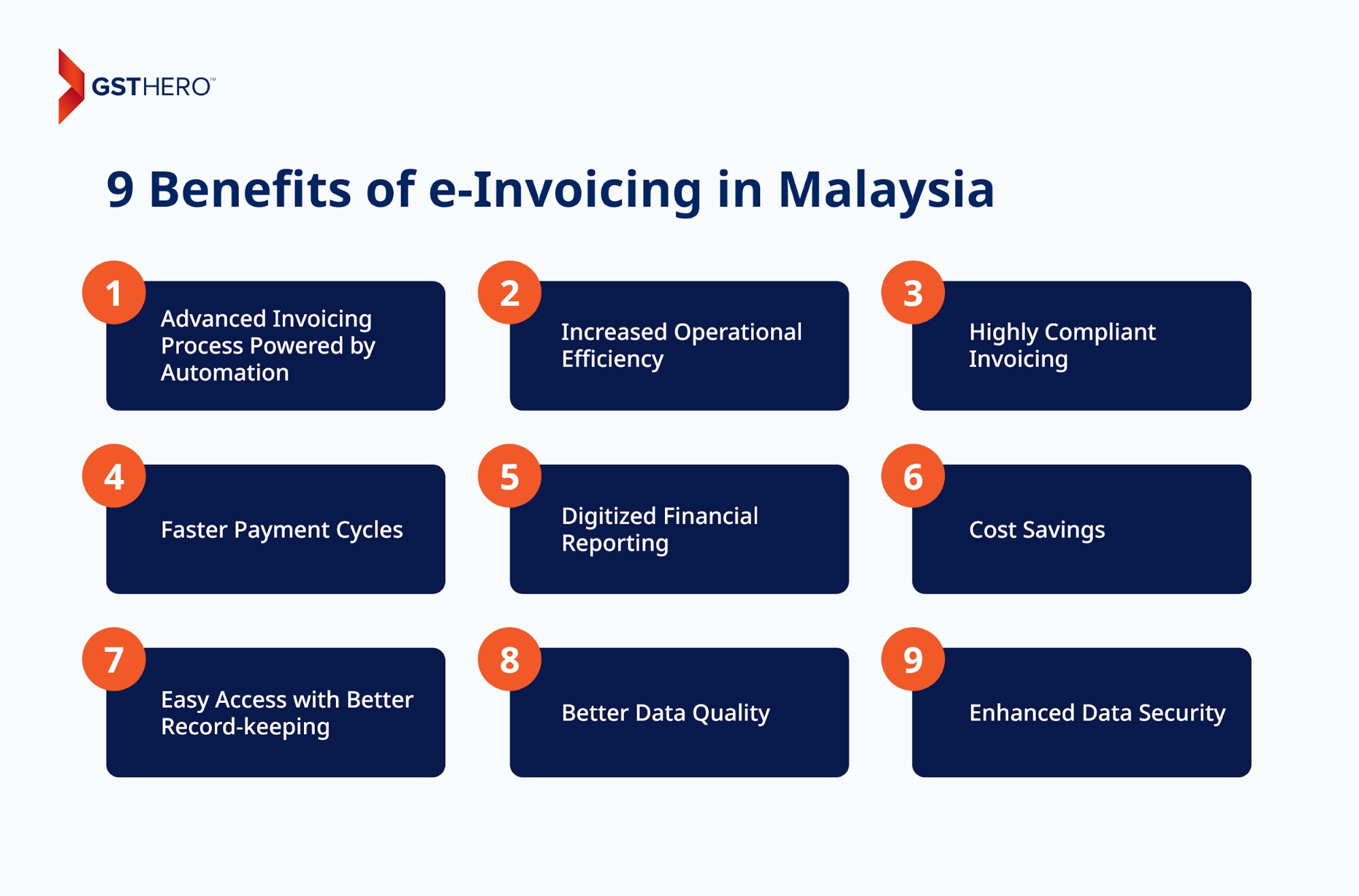
Advanced Invoicing Process Powered by Automation
E-invoicing will promote effortless generation and submission of documents through an automated system. It will prevent slower processing times and risks of manual errors by automating the data entry process.
Implementation of e-Invoicing will allow employees to focus on more important tasks by automating repetitive tasks while ensuring accuracy and compliance.
Increased Operational Efficiency
A faster invoicing process will mean faster deliveries and better operational efficiency for businesses, giving them a competitive advantage.
Highly Compliant Invoicing
As IRBM offers hassle-free integration with MyInvois and API integration, meeting compliance standards with e-invoicing, reducing errors, and ensuring accurate reporting will be much easier for businesses.
Faster Payment Cycles
Since e-invoicing speeds up the submission, validation, and approval of invoices, issuance and payment for invoices will happen much faster. It will benefit both the sellers and buyers, helping improve cash flows and avoid late fees.
Digitized Financial Reporting
With the digitization of e-invoicing, businesses can improve their financial management practices by aligning their reporting and processes with industry standards.
Cost Savings
E-invoicing prevents the need for a paper-based process, and thus, prevents costs for printing, transfer, manual labor, and storage of such paper-based documents. It significantly reduces the amount of money required to generate and manage invoices, helping businesses save on operational costs.
Easy Access with Better Record-keeping
You can store your e-invoices on a cloud-based e-invoicing software, which ensures easy access, hassle-free management, and backup and restore functionality for the invoices. Such record-keeping can prove highly beneficial, especially for/during an audit.
Better Data Quality
With automation, e-invoicing allows you to minimize errors in your data and improve the accuracy of information. It improves the integrity/quality of data in your invoices, enabling faster approval and quick payments.
Enhanced Data Security
As mentioned before, e-invoicing requires secure storage like a cloud-based e-invoicing solution to meet compliance and legal requirements.
Such a solution offers many powerful layers of security for your invoices, prevents data loss or leaks, reduces errors, accelerates invoice approval, and ensures faster payments.
Consequences of Not Generating E-invoices in Malaysia
Failing to comply with the e-invoicing mandate by IRBM can lead to penalties and legal actions in some cases.
The Malaysian Income Tax Act considers the failure to generate e-invoices a criminal offense.
Hence, the e-invoicing Malaysia penalty ranges from RM 200 to RM 20,000 and in some extreme cases, imprisonment for up to six months. Some parties may face both the penalty and imprisonment.
Such strict regulations by the Malaysian government represent their dedication to improving transactional efficiency in the country.
In short, every business conducting the sales of goods or services must generate an e-invoice.
Parties that are Exempted from Implementing E-invoices
The latest guidelines by IRBM specify the parties that are exempted from issuing e-invoices :

- Ruler and Ruling Chief
- Former Ruler and Ruling Chief
- Consort of a Ruler of a State having the title of Raja Perempuan, Sultanah, Tengku Ampuan, Raja
- Permaisuri, Tengku Permaisuri or Permaisuri
- Consort of a Former Ruler of a State previously having the title of Raja Perempuan, Sultanah, Tengku
- Ampuan, Raja Permaisuri, Tengku Permaisuri or Permaisuri
- Government
- State Government and State Authority
- Government Authority
- Local Authority
- Statutory Authority and Statutory Body
- Facilities provided by the above Government or Authority (For example, hospitals, clinics, or multipurpose halls)
- Consular Offices, Diplomatic Officers, Consular Officers, and Consular Employees
Additionally, e-invoices (including self-billed E-invoices) are not required for the types of income or expense mentioned below :
- Employment Income
- Pension
- Alimony
- Zakat
- Scholarship
These exemption lists are subject to review and update by the IRB as and when deemed necessary.
Additionally, certain regulations apply to these exemptions, which you can learn about below -
- Suppliers providing goods or services to those mentioned in the lists above must issue e-invoices according to the specified timeline.
- For transactions involving numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and 13 individuals/parties from the list, suppliers may replace buyer details as per guidelines.
- For transactions involving numbers 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 12 individuals/parties from the list, suppliers are allowed to use a general Tax Identification Number (TIN) in the Buyer’s TIN field as per guidelines.
- The exemptions in the list only apply to individuals/parties, entities owned by them such as companies or partnerships are subject to e-invoicing regulations.
- Regardless of exemptions, all listed individuals/parties are encouraged to implement e-invoicing to support the Malaysian government's digital initiatives.
Cybersecurity Measures Implemented by the IRB in the MyInvois System
The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia/LHDNM will incorporate multiple security solutions inside the MyInvois system to protect the confidentiality and integrity of the data/transactions that are exchanged and stored on the system.
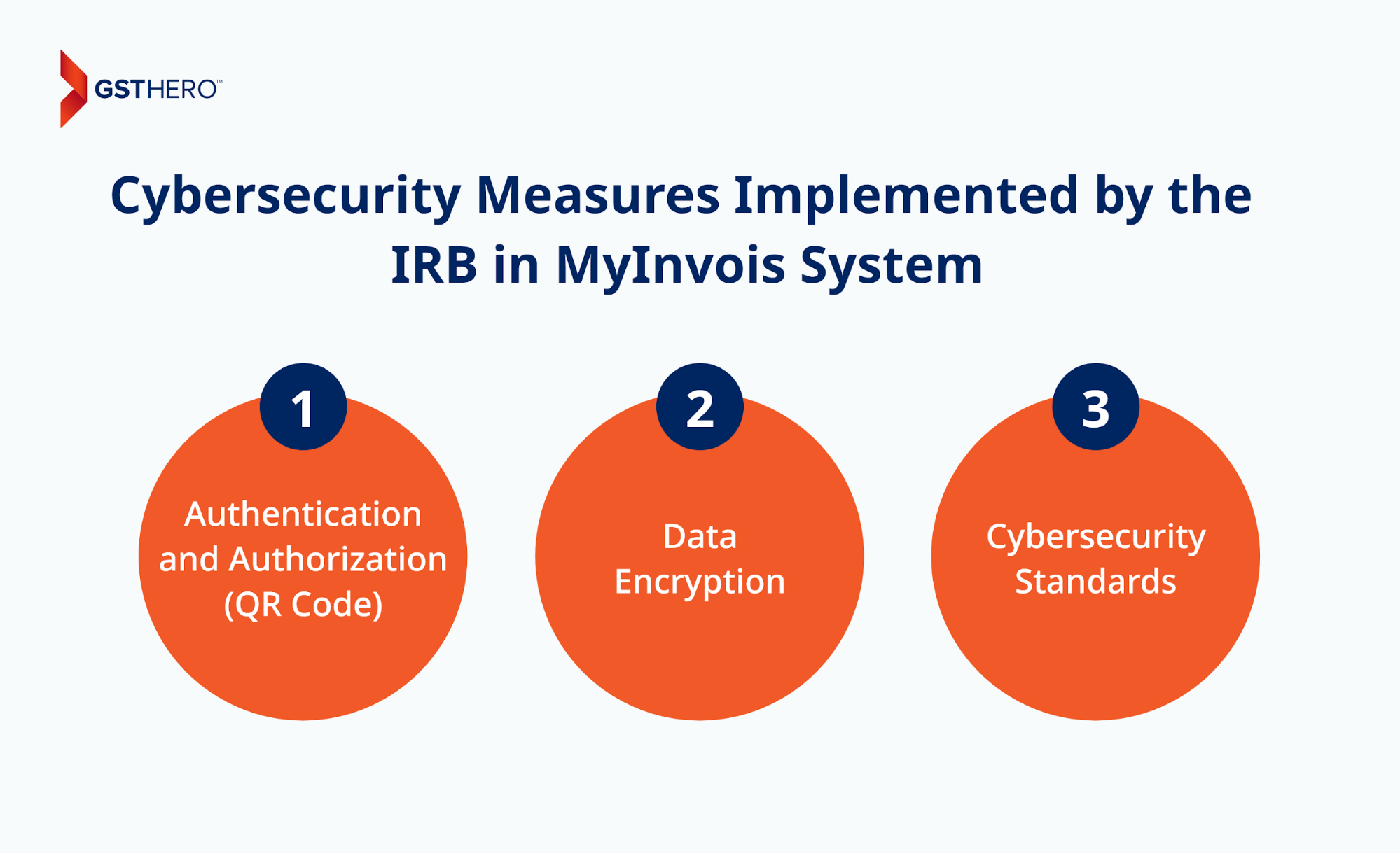
- Authentication and Authorization (QR Code)
Serial Number/Unique Identification Number(UIN) & QR Codes - Data Encryption
- Cybersecurity Standards :
The Inland Revenue Board (IRB) will ensure that the MyInvois System is in compliance and certified with the ISO/IEC 27001 - Information Security Management System (ISMS) and ISO 22301 - Business Continuity Management System BCMS Audit Certification.
Additionally, finding and evaluating the right e-invoicing software in Malaysia is essential to ensure better data security, integrity, and smooth transmission of your invoices.How to Prepare for e-Invoicing in Malaysia?
In Malaysia, e-invoice compliance will require your business to plan and manage the transition to e-invoicing in a strategic manner. Let’s learn how :
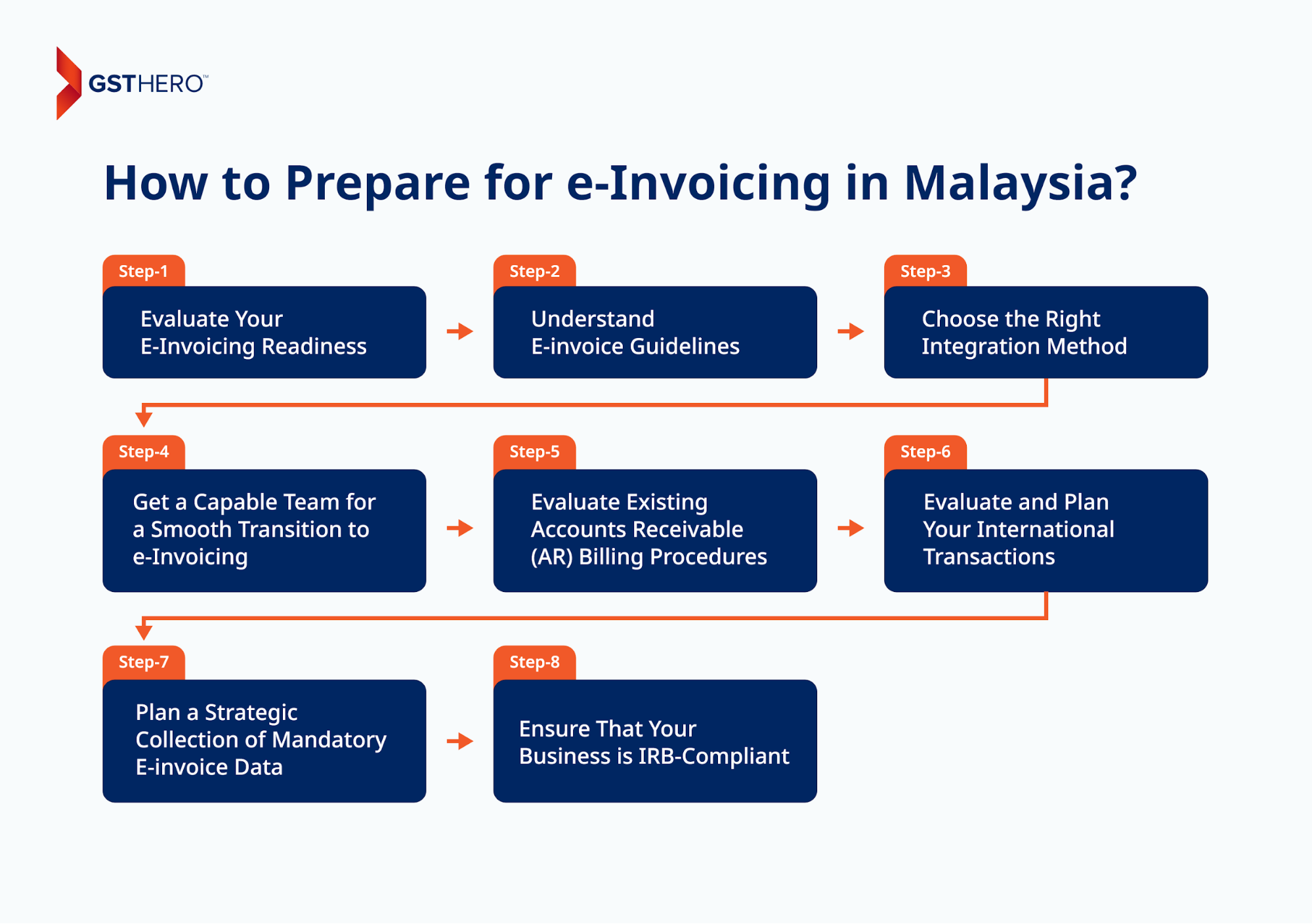
Evaluate Your E-Invoicing Readiness
Analyze and determine the suitability of e-invoicing for your company by evaluating readiness, technological limitations, potential obstacles, and future requirements. You must train all relevant company professionals with the knowledge and tools required to manage the e-invoicing process effectively.
Understand E-invoice Guidelines
Familiarize your organization with e-invoicing regulations, including requirements, Malaysia e-invoice format, and guidelines prescribed by regulatory authorities.
For starters, you can refer to the guideline by IRBM : E-invoicing in Malaysia Guideline.
Ensure compliance with all relevant regulations to streamline the implementation process and avoid potential penalties or setbacks.
Choose the Right Integration Method
The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) provides two options for generating invoices: via MyInvois Portal or API (Direct integration).
Direct integration will allow you to instantly create e-invoices within your ERP system in real time with faster generation capability and less or no errors, especially if you use an advanced tool like GST Hero’s e-invoicing system.
This IRBM-Compliant e-invoicing solution has :
- The processed invoice value of around ₹3 billion or more every year.
- The capability to manage 135 million invoices annually.
- The processing speed of 8 million records in 40 minutes.
Get a Capable Team for a Smooth Transition to e-Invoicing
Get a team of professionals with a broad range of expertise in IT, tax, finance, and project management. This approach ensures comprehensive coverage of all aspects involved in the implementation of e-invoicing, leading to a more effective and seamless transition.
Additionally, the unique insights and skills of such team members will help you capitalize on the e-invoicing initiative through collaboration and innovation.
Evaluate Existing Accounts Receivable (AR) Billing Procedures
Before transitioning to e-invoicing, it's crucial to thoroughly understand your existing Accounts Payable and Account Receivable (AR) billing procedures. Evaluate whether the timing of e-invoice issuance aligns seamlessly with the submission of e-invoice data to the Inland Revenue Board (IRB).
This assessment ensures that your AR billing processes are synchronized with e-invoicing requirements. It will reduce disruptions and ensure compliance with regulatory obligations. Additionally, consider streamlining AR processes where necessary to optimize efficiency and accuracy in e-invoice submission.
Evaluate and Plan Your International Transactions
When dealing with foreign customers, it's necessary to have a proper plan for self-issuing e-invoices for international transactions. You must inspect and evaluate how your system currently manages these transactions to identify any potential challenges or areas for improvement.
Ensure that your system complies with international invoicing standards and regulations, considering factors such as currency conversion, language requirements, and cross-border tax implications.
Additionally, explore opportunities to streamline the e-invoicing process for foreign transactions, such as integrating multi-currency support or implementing automated translation features.
It will help you effectively manage e-invoicing for your foreign customer base and enhance overall operational efficiency. Also, if you incorporate such digital invoice solutions, Malaysia’s IRB will recognize your business as a highly compliant e-invoicing practitioner.
Plan a Strategic Collection of Mandatory E-invoice Data
To ensure regulatory compliance with e-invoicing requirements, it's crucial to develop a comprehensive strategy for collecting essential data fields. This includes but is not limited to a unique identification number, name, and address.
You must also collect other crucial information mandated by IRBM to facilitate seamless e-invoice processing and compliance verification.
Explore methods for securely storing and managing collected data to safeguard sensitive information and uphold data privacy standards.
Ensure That Your Business is IRB-Compliant
Like most countries, Malaysia will have its own set of laws and regulations for e-invoicing.
You must ensure your e-invoicing practices comply with these laws and regulations to ensure 100% compliance and avoid any financial/legal consequences.
Which Countries Are Already Using E-invoicing?
While e-invoicing in Malaysia may be a recent practice/news, it is already a well-established mandate in many countries worldwide. Let’s learn a bit more about these highly compliant e-invoicing countries.

United States of America (USA)
The US has been way ahead when it comes to utilizing e-invoicing, where some instances of usage date back to the late 1990s and early 2000s. However, it officially started using e-invoice sometime between 2002 and 2004.
While it is not mandatory in the US, electronic invoicing for small businesses and large enterprises is a highly recommended practice in the country for better transparency and operational efficiency.
Australia
Much like in the US, e-invoicing is available in Australia, but not mandatory. Various guidelines such as buyer’s consent for usage and digital signature are given for the use of electronic invoices in Australia.The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) is the tax authority for e-invoicing in Australia.
India
The e-invoicing system under GST was officially implemented in India on 1st October 2020, applicable to taxpayers with a turnover of more than 500 Crores.
Since the introduction of the the latest amendment in August 2023, all Indian businesses registered under GST and with a turnover of more than 5 Crores, are required to generate an e-invoice.
The tax authority for e-invoicing in India is the Invoice Registration Portal and GST System.
Japan
E-invoicing is not mandatory in Japan as well, but it has introduced a new model based on the PEPPOL network, promoting the use of qualified invoices powered by PEPPOL e-invoicing. The tax authority for e-invoicing in Japan is the National Tax Agency.
Some other countries where e-invoicing is in full effect or growing are Argentina, Brazil, Greece, Canada, Iceland, Italy, Colombia, invoicing, Germany, Mexico, New Zealand, Norway, and many more.
Malaysia is only a few years away from becoming a part of this growth by benefiting from many uses of e-invoices.
Challenges of e-Invoicing for Businesses in Malaysia
The e-invoicing mandate by IRBM is set to redefine the ways of conducting business in Malaysia in the most lucrative ways. However, every change comes with adaptation and transition challenges. Likely, many businesses may face these challenges after the implementation of e-invoicing in Malaysia.
Let’s look into some of them to anticipate and avoid them :
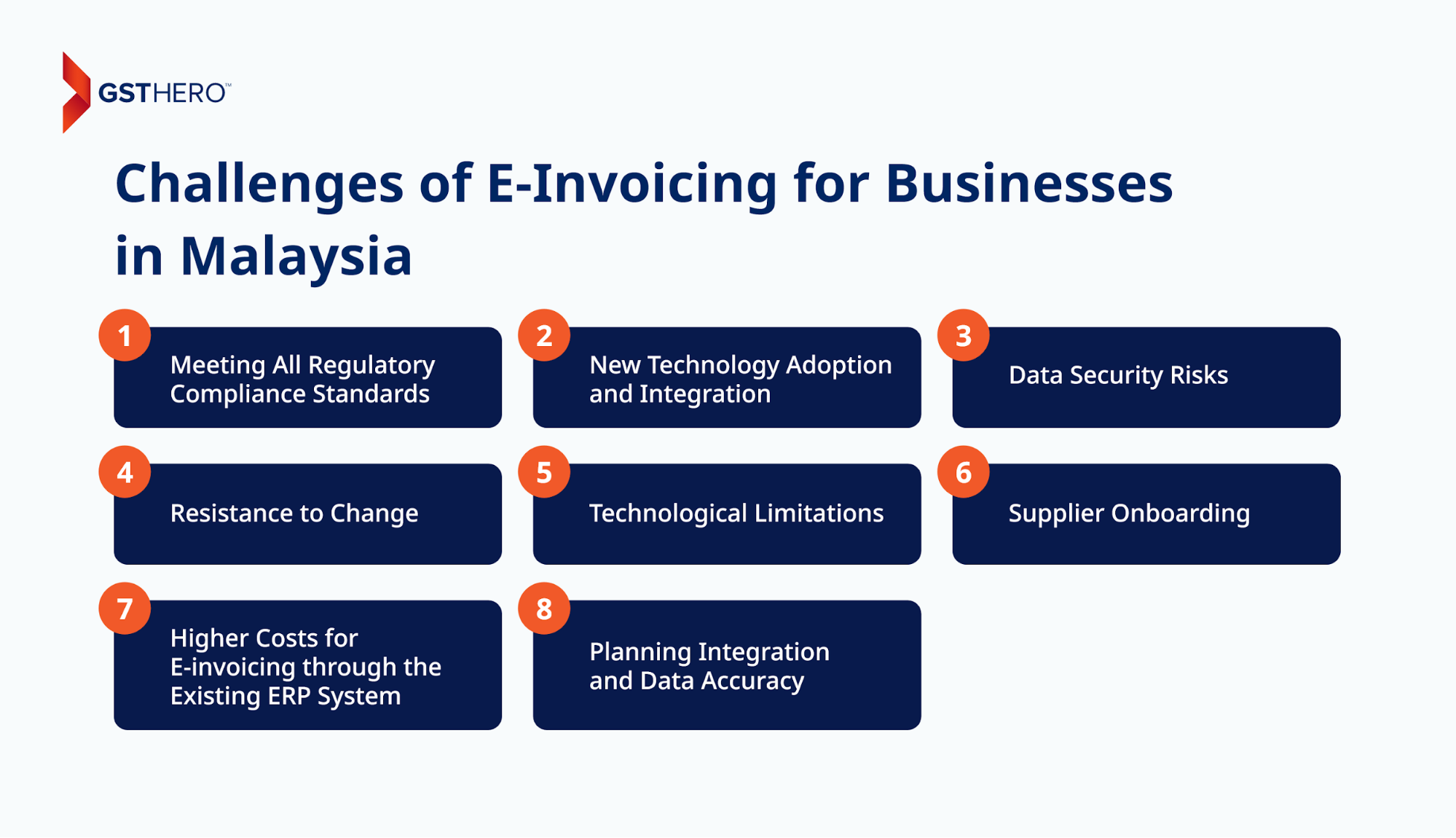
Meeting All Regulatory Compliance Standards
Since IRBM is implementing e-invoicing regulations in a phased manner, businesses are likely to struggle while tracking and meeting all necessary compliance requirements.
Large businesses with a vast infrastructure will face these challenges the most, but it is just as likely for small and medium-sized businesses.
New Technology Adoption and Integration
While the migration from traditional invoicing to electronic medium will be highly beneficial, it will not be easy to accomplish for every business. Choosing and adopting new technologies with the right automation capabilities will be a hassle.
Additionally, integration with existing systems could prove complicated due to compatibility and scalability issues. Training the company individuals to transition to the new system will be another challenge.
Data Security Risks
With the rise of cybersecurity threats, ensuring your data is safe with electronic invoicing is a major challenge. Businesses will need to address these problems before and during the transition as invoices contain a lot of sensitive and confidential information, leakage of which could have some severe consequences.
A secure cloud-based e-invoicing solution is the right option to deal with these challenges. However, businesses must do their research, compare different solutions, and test them to ensure the solutions can offer the best level of security for their invoices.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common human trait all over the world, and it can hamper the transition to e-invoicing as employees familiar and comfortable with the traditional invoicing process may not accept and adapt to the new electronic system so quickly or with enthusiasm.
Every business will need to anticipate and deal with this internal issue in a way that is most suitable, appropriate, and beneficial for them.
Technological Limitations
Some businesses, specifically small or micro ones, will face technological limitations while transitioning to e-invoicing as they have limited IT infrastructure.
Planning Integration and Data Accuracy
Integrating IRBM’s e-invoicing system with an ERP will be a complex task as it requires thorough planning, customization, and the right compatibility. Without it, it will be difficult for businesses to maintain accuracy, effortless data exchange, operational efficiency, and compliance in their e-invoicing process.
Supplier Onboarding
Getting suppliers to transition from traditional invoicing to electronic invoicing will be challenging, especially for businesses with a vast list of suppliers. Acceptance from suppliers will only be half the challenges, getting them aligned with the new e-invoicing process and technology will be a major hassle.
Higher Costs for E-invoicing through the Existing ERP System
Your existing ERP system may prove to be expensive after the transition to e-invoicing. You must evaluate and determine whether those costs are acceptable for your business before the migration.
Additionally, the electronic invoicing software you choose for e-invoicing may also be costly.
Ideally, any best invoice software Malaysia has to offer would be affordable and will easily integrate with your ERP systems.
While there are many challenges associated with e-invoicing as there are with any change, its benefits far outweigh the challenges. Choosing the right e-invoicing solution will ensure your business never experiences such negative effects or damages.
Solution to Overcome All These Challenges
When you integrate GST Hero (a reliable e-invoicing solution) into your business operations, you'll experience significant time and workload savings.
Our solution will prevent the challenges associated with migrating data from your current system by offering comprehensive guidance on e-invoicing implementation in Malaysia and support for data migration.
For expert assistance and a detailed understanding of e-invoicing options tailored to your company's needs, consider reaching out to GST Hero.
Our experts can provide thorough explanations and guidance through the transition process, ensuring your organization is well-prepared for the future of invoicing.
We offer a cloud-based invoicing solution with benefits like -
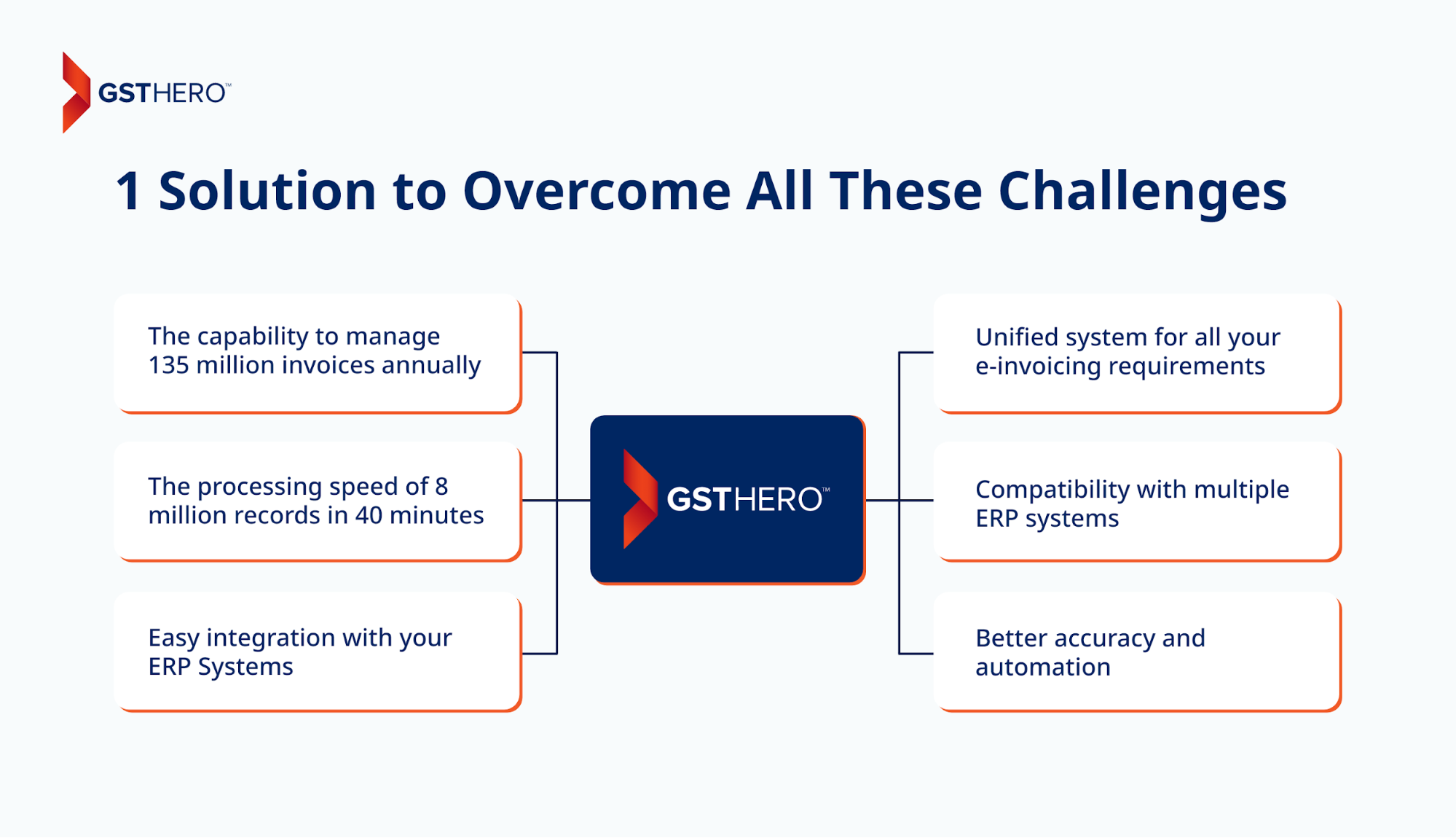
- The capability to manage 135 million invoices annually
- The processing speed of 8 million records in 40 minutes
- Easy integration with your ERP Systems
- Better accuracy and automation
- Compatibility with multiple ERP systems
- Unified system for all your e-invoicing requirements
How can GST Hero help with e-Invoicing in Malaysia?
GSTHero provides one of the most user-friendly e-invoicing solutions in Malaysia.
It will effortlessly connect your ERP/POS system with the IRBM cloud, ensuring 100% IRBM compliance.
The key features of GSTHero e-invoicing include -
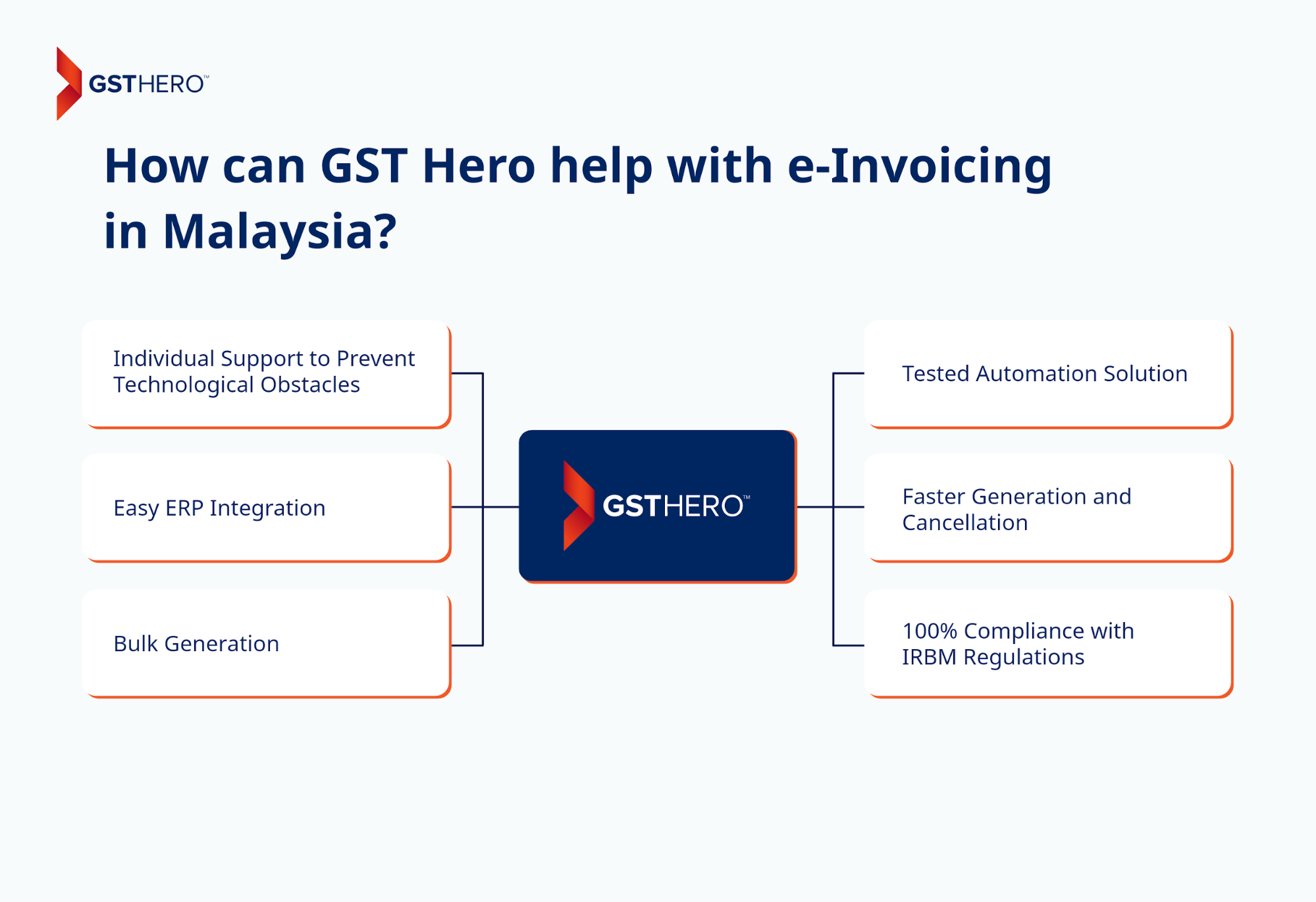
Individual Support to Prevent Technological Obstacles
You get support from a certified expert who will provide step-by-step guidance for e-invoicing in Malaysia through GST Hero and help you meet all compliance standards.
Easy ERP Integration
GSTHero facilitates quick integration with multiple ERPs like SAP, Tally, Oracle, Microsoft, and Custom ERPs to ensure compliance faster.
Bulk Generation
GST Hero has a processing speed of 8 million records in 40 minutes, helping you generate bulk invoices within minutes.
Tested Automation Solution
With GST Hero’s automation, you can expect better speed (operational efficiency), accuracy, and prevention of all manual errors.
Faster Generation and Cancellation
You can rapidly generate and cancel E-invoices with a single click.
100% Compliance with IRBM RegulationsThe e-invoicing solutions are 100% compliant with IRBM’s regulations for e-invoicing in Malaysia. GSTHero is a reliable partner in your journey towards effortless e-invoicing and compliance in Malaysia.Conclusion
Meeting all compliance requirements for e-invoicing in Malaysia may seem complicated at first, but the only obstacles you truly have to overcome are finding the right e-invoicing solution providers and familiarizing your business with e-invoicing. Reading this article carefully will help you with the latter.
For the former, it’s ideal to evaluate e-invoicing requirements for your business and compare the best e-invoicing solutions in Malaysia to identify the most suitable in terms of the quality of services offered and the costs.
Ideally, a solution like GST Hero will serve your e-invoicing requirements well, offering benefits like compliance with IRBM regulations, faster processing speed, no errors with automation, faster payment cycles, better integration capabilities, and much more.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
GSTHero is the ideal solution for effortless and secure e-invoicing in Malaysia.
Key benefits include :
- 100% IRBM Compliance
- Individual Support to Prevent Technological Obstacles
- Easy ERP Integration
- Bulk Generation - processing speed of 8 million records in 40 minutes.
- Tested Automation Solution
- Faster Generation and Cancellation
It depends on the turnover of your business. Here’s the implementation timeline for your reference :
1st August 2024 : E-invoicing will be in effect for taxpayers with an annual revenue/turnover of more than RM 100 million.
1st January 2025 : E-invoicing will be in effect for taxpayers with an annual revenue/turnover of more than RM 25 million and within RM 100 million.
1st July 2025 : It will be in effect for all taxpayers (small, medium, or large).
The Peppol Framework will be the leading solution in managing the e-invoicing system in Malaysia. Any software businesses use for e-invoicing in Malaysia will need to be Peppol-certified software.
For effortless and IRB-compliant adoption, it’s best to get assistance from a Peppol-certified e-invoicing solution provider in Malaysia. Such providers will ensure that your transition from traditional to electronic invoicing happens without any hassles and meets the standards of the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia.
E-invoicing in Malaysia is only mandatory for B2B, B2C, and B2G transactions.Refer to this to learn about parties that are exempt from e-invoicing.
A Digital Certificate, used for signing and issued by the IRB using taxpayers’s TIN, is mandatory for e-invoicing in Malaysia. It has a validity of 3 years and is crucial for verifying authenticity and compliance with IRBM.
No, e-invoicing in Malaysia is mandatory for both domestic and international transactions.
A Continuous Transaction Control (CTC) model, connected to the Peppol network for quicker validations.
According to the IRBM, A valid invoice in Malaysia should contain 53 E-invoice mandatory fields, including seller & buyer details, item description, quantity, price, tax, total amount, payment details, etc.
These fields are grouped into 9 categories :
- Address
- Business Details
- Contact Number
- Invoice Details
- Parties
- Party Details
- Payment Info
- Products / Services
- Unique ID Number
The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia/LHDNM will implement various security protocols for e-invoicing in Malaysia, including:
- Authentication and Authorization
Serial Number/Unique Identification Number(UIN) & QR Codes - Data Encryption
- Cybersecurity Standards :
The Inland Revenue Board (IRB) will ensure that the MyInvois System is in compliance and certified with the ISO/IEC 27001 - Information Security Management System (ISMS) and ISO 22301 - Business Continuity Management System BCMS Audit Certification.
After the IRBM receives the e-invoice, the verification of the mandatory field happens for validation. Post-validation, the buyer and supplier get notification about the validation and easy access to the summary of all invoices on the MyInvois portal.
Please refer to the guidelines by IRBM here to issue invoices for disbursals and reimbursements in Malaysia.
Yes, you can cancel the e-invoice within 72 hours after generation.
The Peppol System and Peppol-certified software solutions.
Not complying with the e-invoicing mandate by IRBM will lead to penalties and legal actions.
The penalty ranges from RM 200 to RM 20,000. In rare cases, imprisonment for up to six months, whereas some parties may face both the penalty and imprisonment.
E-invoicing in Malaysia will align effortlessly with the global standards to facilitate cross-border trade and compliance.
Compliance with Global Frameworks
Malaysia's e-invoicing system is designed to comply with international frameworks like the PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement Online), widely adopted in Europe and other parts of the world.
Technology Adoption
Malaysia’s system utilizes advanced technologies like cloud computing, API integration, and secure data transmission methods. These are in line with international best practices, ensuring secure and efficient invoice processing.
Regulatory Framework
The Malaysian government, through the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM), has established a regulatory framework that mandates the use of e-invoicing for businesses. This approach is similar to that in countries like Italy and Germany, where e-invoicing is also legally required for tax reporting.
Standardization and Interoperability
Malaysia is working towards standardizing e-invoicing formats and protocols to ensure interoperability with other countries' systems. This is crucial for international trade and is a core principle of global e-invoicing systems.
Adoption and Implementation Pace
While Malaysia is rapidly adopting e-invoicing, some countries have been using e-invoicing for a longer time. This means Malaysia can learn from the challenges and successes of these nations to implement a robust and efficient e-invoicing system.
Overall, Malaysia is a few years away from getting ahead of the curve in e-invoicing by learning from the e-invoicing implementation/transition mistakes of many countries that are now global leaders in e-invoicing.
Benefits of e-invoicing in Malaysia include :
Advanced Invoicing Process Powered by Automation
Effortless generation and submission of documents, faster processing times, and no manual errors.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Faster deliveries, better operational efficiency, and a competitive advantage with digital transformation.
Highly Compliant Invoicing
Effortless IRBM-compliant e-invoicing, reduced errors, easy API integrations, and accurate reporting.
Faster Payment Cycles
Faster invoice issuance and payments - Improved cash flows and no late fees.
Digitized Financial Reporting
Improved financial management for businesses due to compliance with industry standards.
Enhanced Data Security
As mentioned before, IRBM will incorporate various security solutions like Authentication and Authorization, Data Encryption, and real-time compliance with Cybersecurity Standards. It will ensure better security and quality for all data in e-invoicing.
Other benefits include significant Cost Savings, Easy Access with Streamlined Record-keeping, and Better Data Quality.
Yes, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia has already provided comprehensive guidelines for transitioning from traditional invoicing to electronic invoicing. You can find the guidelines here.
The Continuous Transaction Control model includes a set of system protocols enabling real-time tracking of transactions and financial data by the official tax authorities of a country to verify compliance of a business through electronic invoicing.
Benefits of the CTC Model :
Real-time Data Access
CTC enables tax authorities to access transaction data in real-time or near real-time, allowing for immediate insight into financial activities while preventing errors. This facilitates more accurate and timely tax assessments and reduces the lag time in collecting relevant financial information.
Increased Compliance and Reduced Fraud
By automatically reporting transactions as they occur, the CTC model minimizes the opportunity for tax evasion and fraud. It ensures that all transactions are recorded and reported correctly, reducing the risk of errors or manipulation of financial records.
Improved Efficiency
Automating the process of transaction reporting through CTC systems reduces the administrative burden on businesses. It streamlines the tax reporting process, saving time, and resources that would otherwise be spent on manual compliance tasks.
Enhanced Data Quality and Accuracy
Continuous transaction controls help improve the accuracy and quality of financial data. Since transactions are captured and transmitted electronically, the chances of manual errors are significantly reduced, leading to more reliable financial reporting.
Faster Audits and Tax Assessments
With real-time data at their fingertips, tax authorities can conduct audits more efficiently. The need for extensive manual audits is diminished since authorities can analyze transaction data as it is generated. It leads to quicker tax assessments and faster resolution of tax disputes.
Better Business Intelligence
The data collected through CTC can provide valuable insights into market trends and business performance. Companies can leverage this data for better decision-making, financial planning, and strategic development.
Increased Transparency
CTC systems promote transparency in the business environment, as all transactions are recorded and can be traced back. This increases trust among stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, and regulatory bodies.
Cost Savings
Over time, the automation and streamlining of tax reporting and compliance processes can lead to significant cost savings for businesses and tax authorities alike, reducing the need for manual interventions and corrections.

