At GSTHero we constantly try to influx GST-related information for the ease of the GST payers in India. Over recent months, there has been scant attention paid to the intricacies of the GST procedures like GST Audit and Assessment under GST. These two processes in the GST regime play a vital role when disparities arise between a taxpayer's liabilities and the amount remitted. Hence, in this article, we have focused on the GST Assessment procedure so that GST payers can familiarize themselves with GST compliance.
What is an Assessment under GST?
Assessment under GST refers to the process of examining the tax liability of a taxpayer based on the information provided in their returns and other relevant documents. It plays a significant role in ensuring compliance with GST laws and regulations and maintaining the integrity of the tax system.
In simpler words, Calculating the GST taxpayer's liability is an assessment under GST.
Who carries out the assessment under GST?
Taxpayers or GST officials (varies depending on the type of the assessment).
GST Assessment Procedure
The GST assessment procedure is a systematic process that ensures the accuracy and compliance of tax returns filed by taxpayers. Following is a detailed explanation of the steps involved :
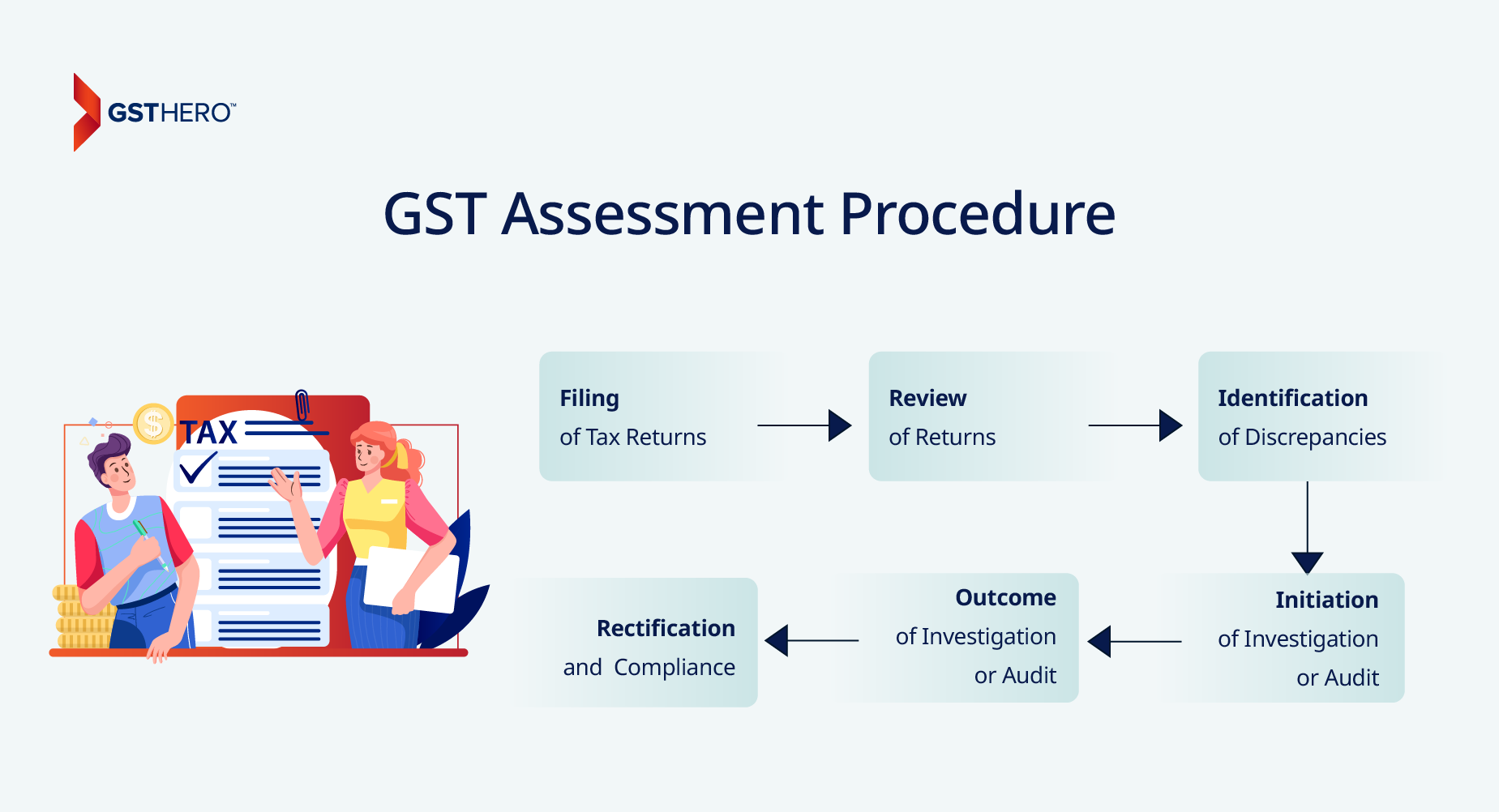
- Filing of Tax Returns : The process begins with taxpayers filing their tax returns. These returns include comprehensive details about the taxpayer’s income, expenses, and tax liability. It’s the responsibility of the taxpayer to ensure the accuracy of these details.
- Review of Returns : Once the tax returns are filed, they are reviewed by the tax authorities. This review process involves checking the returns for any discrepancies or inaccuracies. The authorities verify the accuracy of the information provided in the returns, including the taxpayer’s income, expenses, and tax liability.
- Identification of Discrepancies : If any discrepancies are found during the review process, the tax authorities identify these issues. These discrepancies could be due to errors in the calculation of tax liability, incorrect information about income or expenses, or non-compliance with GST laws and regulations.
- Initiation of Investigation or Audit : If discrepancies are found in the tax returns, the tax authorities may initiate an investigation or audit. This is a more detailed examination of the taxpayer’s records and transactions to verify the accuracy of the tax returns and determine the correct tax liability.
- Outcome of Investigation or Audit : The outcome of the investigation or audit could lead to several scenarios. If the taxpayer’s returns are found to be accurate, no further action is taken. However, if discrepancies are confirmed, the taxpayer may be required to pay additional taxes, penalties, or fines. In severe cases of non-compliance, legal action may be taken against the taxpayer.
- Rectification and Compliance : After the investigation or audit, the taxpayer is allowed to rectify the discrepancies and comply with the GST laws and regulations. This could involve paying any additional taxes owed, correcting errors in future tax returns, or implementing measures to ensure compliance with GST laws and regulations.
By understanding and following the GST assessment procedure, taxpayers can ensure they are in compliance with GST laws and regulations, avoid penalties, and contribute to the integrity of the tax system. It’s always recommended to consult with a tax professional or advisor to ensure accurate and compliant tax returns.
Types of assessment under GST

- Self-Assessment :
Self-assessment is the cornerstone of the GST regime, where taxpayers are entrusted with the responsibility of assessing their tax liabilities accurately. Under this method, taxpayers calculate and pay their taxes based on the details furnished in their GST return filing. It not only emphasizes voluntary compliance and transparency in tax reporting but also helps taxpayers identify any flaws in their GST return status. - Summary Assessment :
Summary assessment is conducted by GST officials to verify the correctness of the taxpayer's self-assessment. It involves a preliminary examination of the taxpayer's GST return filing and documents to ascertain any discrepancies or errors. Summary assessment helps in identifying potential tax evasion and ensuring the accuracy of tax filings. - Scrutiny Assessment :
Scrutiny assessment is a detailed examination of the taxpayer's records and documents by the GST authorities to verify the accuracy and completeness of the GST return filing. It may be initiated based on specific risk parameters or discrepancies identified during the summary assessment. Scrutiny assessment aims to detect any non-compliance with GST laws and regulations and take appropriate corrective measures. - Best Judgment Assessment :
Best judgment assessment is carried out by GST authorities when a taxpayer fails to furnish the required documents or information for assessment. In such cases, the assessing officer relies on their best judgment to determine the taxpayer's tax liability based on available information and relevant factors. Best judgment assessment serves as a last resort to ensure tax compliance in cases of non-cooperation or non-compliance by taxpayers.
Importance of Assessment under GST
Assessment under GST holds immense significance for small and medium business GST taxpayers in India due to the following reasons :
Compliance and Transparency :
Proper assessment ensures compliance with GST laws and regulations, fostering transparency and trust in the tax system. It enables taxpayers to fulfill their tax obligations accurately and on time, thereby contributing to the overall integrity of the GST regime.
Detection of Tax Evasion :
Through thorough assessment procedures such as summary and scrutiny assessment, tax authorities can identify instances of tax evasion or underreporting of income by taxpayers. This helps in preventing revenue leakage and maintaining the revenue neutrality of the GST system.
Fair Taxation :
The assessment ensures that taxpayers pay their fair share of taxes based on their actual turnover and transactions. It prevents unfair advantage or undue tax benefits for certain taxpayers and promotes equitable taxation across all sectors and businesses.
Legal Compliance :
Compliance with assessment procedures is essential to avoid penalties, fines, or legal action by tax authorities. By adhering to the assessment requirements under GST, taxpayers can mitigate the risk of non-compliance and safeguard their business interests.
Prevention is better than cure!
In the previous section, we mentioned that the self-assessment is the first and most important type of GST assessment which has to be done by the taxpayer. To carry out this self-assessment a business needs to have some checks and balances in place to identify the disparities between their actual GST liabilities and what they are paying.
When businesses rely on their existing ERPs and their checkpoints, they try to bypass the step of auditing their GST returns for the month.
The ERP systems do indeed have few checkpoints in place, but an internal GST audit benefits your business more than the standard checkpoints in your ERP system.
An internal audit under GST will act as a self-assessment under GST and shall help businesses to be compliant with the dynamic GST laws in India.
Following are some of the things that the ERP is INCAPABLE of doing & an Internal GST Audit tool is CAPABLE of doing :
- Identifying ineligible ITC & potential threats for all your sub-branches all at once
- Identify risk exposure & suggest corrective actions on pending liabilities.
- Generate a ‘Bird’s Eye’ view of the complete GST return filing of all the branches registered under the single PAN.
Following are some of the significant edges that the GST Audit tool has over traditional MIS reports :
- The interactive dashboards help the decision-makers to analyze the data in less time.
- Granular-level reporting is done automatically, which, if done manually, is a very tedious and time-consuming task.
- Error introduction in data is shunted as the complete auditing and reconciling process will be automated.
- GSTHero is a Government of India authorized GST Suvidha Provider and can fetch the authenticated GST data directly from the GSTN. This data helps the tool to analyze the previous years' return filing trends and identify if there are any possible risks with this approach.
- Traditional MIS reports DO NOT focus on the ‘Predictive Analysis’ part of the data.
For these reasons, a GST Audit tool like GSTHero ThirdEye is essential to flag the risks and suggest corrective actions. In addition, this tool saves the resource drain on paying penalties and interest if the GST compliance requirements are not met.
In a nutshell…..
Understanding the Assessment is crucial for businesses, especially those dealing with exempt goods or services, or those registered under the composition scheme. It helps ensure compliance with GST laws and avoid penalties. By undergoing the appropriate assessment, businesses can maintain accurate records of their transactions, which is essential for filing GST returns.
Keep visiting GSTHero for more updates.
Until the next time…

