Probably by now we all are mostly aware of the existence of the term ‘Composition Scheme’ under Goods and Services Tax (GST). But due to the frequently changing GST law and complication involved therein, even the simple looking ‘GST Composition Scheme’ has become quite complex.
Importantly, the GST composition scheme is voluntary/ optional scheme. In order to analyze whether to opt under the scheme or not, it is firstly vital to understand the structure of the composition scheme under GST; privileges available under the scheme and merits as well as demerits of the scheme.
The present article tries to clear up all the complexations involved under the GST Composition Scheme for service providers and briefly explains the merits and demerits of the scheme.
What is Composition Scheme under GST
Before going into the nitty-gritty of the structure of the composition scheme, first of all, let us list down the categories of composition taxable persons who cannot opt for the composition scheme. The list is briefed hereunder-
Who Can opt for a Composition Scheme
So now, let us look into the categories of persons who can opt for a composition scheme list is covered in this GST composition scheme article. Referring to notification no. 14/2019- Central Tax dated 7th March 2019, categories of the person eligible to opt under compositions scheme are-
- A person registered under north-eastern states and Himachal Pradesh having aggregate turnover in the preceding financial year is less than INR 75 Lakhs; or
- A person registered under any other states having aggregate turnover of less than INR 150 Lakhs in the preceding financial year.
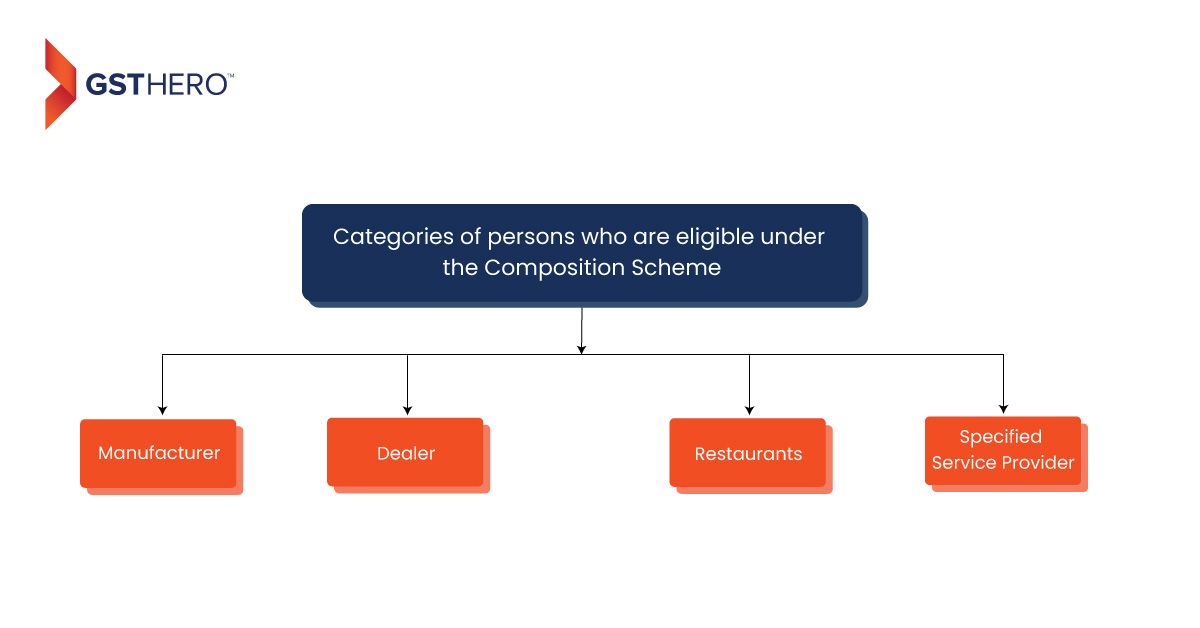
Notably, from 1st April 2019, vide notification no. 2/2019-Central Tax (Rate) dated 7th March 2019, service providers, having turnover up to INR 50 Lakhs, was for the first time given the opportunity to avail the benefit of the composition scheme.
After briefly understanding the eligibility and ineligibility of the composition scheme, let us now understand the conditions to be satisfied under the scheme.
The conditions to be satisfied by the person wiling to opt under the scheme, as prescribed under section 10(2) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, are briefed hereunder-
Condition 1 – The person should not be engaged in supplying goods or services which is not taxable under GST
Condition 2 – The person should not be engaged in carrying out inter-state supply of goods or services
Condition 3 – The person should not be a non-resident taxable person or a casual taxable person
Condition 4 – The person should not be engaged in supplying goods or services via e-commerce operator liable to collect TCS under section 52 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017.
Condition 5 – The person can supply services only to the extent of higher of 10% of turnover or INR 5 Lakhs.
Condition 6 – The person should not be engaged in manufacturing goods like ice cream and other edible ice; pan masala; all goods like Tobacco and manufactured tobacco classified under heading 24.
Now, let us understand the procedure to be followed for opting under the composition scheme. The following table simplifies the procedure-
Situation | Procedure to be followed for opting under the composition scheme |
|---|---|
The person is applying for fresh GST registration and wants to directly opt for a composition scheme | As per rule 3(2) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017, such a person just has to select the option in Part B of application Form GST REG-1. |
The person is already registered under GST and wants to opt for a composition scheme | As per rule 3(3) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017-
|
Composition Dealer Privileges
Following are some of the important privileges available to the person who has opted under the composition scheme-
1. Lower GST rates
As per section 10(1) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 read with rule 7 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017, the composition scheme dealer will have to pay GST at lower rates.
The GST rate on services applicable to the composition scheme dealer are tabulated hereunder-
Sr. No. | Classification of business | GST Rate |
1 | Manufacturer | 1% [0.5% CGST and 0.5% SGST] |
2 | Specified restaurant services | 5% [2.5% CGST and 2.5% SGST] |
3 | Trader or any other eligible supplier | 1% [0.5% CGST and 0.5% SGST] |
4 | Service providers | 6% [3% CGST and 3% SGST] |
1. Lesser filing of GST returns
The filing of GST return is simplified under the composition scheme. Accordingly, the composition dealer is required to furnish fewer GST returns, as per the table detailed below-
Forms | Reference of respective rule | Description | Return filing duration | Due date of filing of return |
Rule 62(1)(i) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017 | Statement for payment of self- assessed tax | Quarterly basis | Within 18 days of the month following the quarter | |
Rule 62(1)(ii) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017 | Return for the Financial Year of the person who has opted for composition levy under GST | Annual | Within 30th April of the succeeding Financial Year |
Advantages of the GST Composition Scheme
Various merits of the compositions scheme are briefed hereunder-
Simpler Compliance
The scheme notably reduces the compliance burden for small enterprises by simplifying tax payments and easing return filing obligations.
Lower Tax Liability
Businesses registered under the composition scheme benefit from lower tax rates, decreasing their tax burden and liberating capital for business expansion. The following flowchart explains how the same is possible-
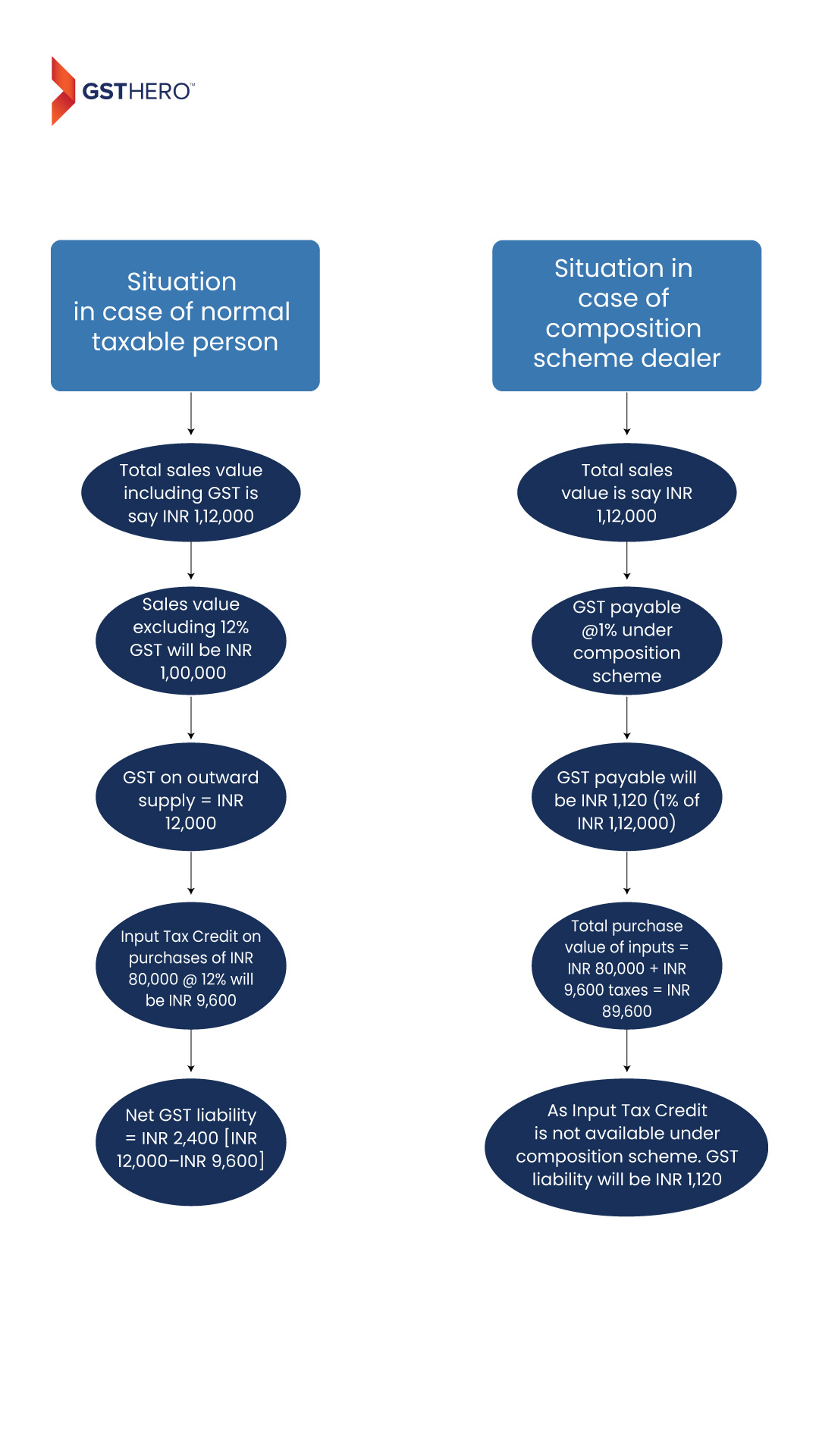
Less payment of GST and non-blockage of funds under input tax credit results into high liquidity/ cash flow for composition scheme dealer.
Ease of Doing Business
With the composition scheme, businesses can concentrate on core activities rather than grappling with intricate tax processes, enhancing overall operational ease.
Disadvantages of the GST Composition Scheme
Similar to two sides of the coin, even a composition scheme involves both advantages and disadvantages. After briefly understanding the merits, let us analyze the demerits of the composition scheme
Non-availability of input tax credit
Those under the composition scheme can't claim input tax credit on purchases. This raises input costs as purchase tax can't be offset against the output tax.
Restriction on Certain Goods
Certain items like alcohol cannot be supplied by composition scheme users, limiting their business scope.
Less preferred
GST registered person is less likely to prefer buying from the composition scheme dealer since GST involved in the transaction is not available to the buyer as an input tax credit. Further, since the dealer is not allowed to collect any amount in terms of GST, the possibility is more that the dealer will increase the basic purchase price and hence the same will probably turn out to be costlier.
Limitation of territorial business
Composition scheme taxpayers are not allowed to engage in inter-state sales transactions. Expansion beyond their home state is restricted.
GST Composition Scheme Synopsis
The gist of the entire article is summarized here under
Eligibility under the Composition Scheme | Person registered under north-eastern and Himachal Pradesh having annual turnover of less than INR 75 Lakhs in the preceding Financial Year. |
Ineligibility under the Composition Scheme |
|
Rate of GST under the Composition Scheme |
|
GST Return filing under the Composition Scheme |
|
Merits of the Composition Scheme |
|
Demerits of the Composition Scheme |
|

